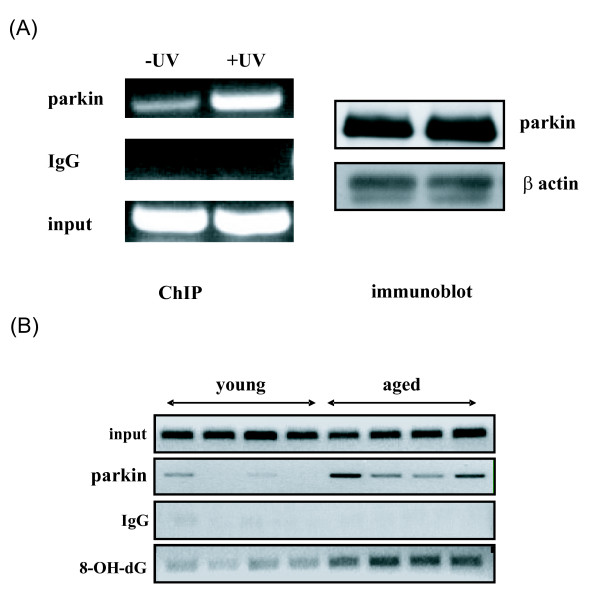
Figure 2.
Parkin interacts with damaged DNA. (A) Parkin was co-transfected in HeLa cells with a calmodulin 1 promoter construct under control conditions (-UV) or after the calmodulin construct was damaged by UV irradiation in vitro (+UV)(100 J/M2). To determine whether parkin interacts with damaged DNA, parkin was immunoprecipitated followed by PCR amplification of the calmodulin promoter construct. Note the markedly increased co-precipitation of parkin with DNA damaged by UV irradiation. Input DNA, non-specific IgG controls, and parkin, β-actin immunoblots are shown. (B) Parkin binds to chromatin in the aging human brain. ChIP assays were performed on postmortem human cortical samples with anti-parkin or anti-8-oxoguanine followed by PCR amplification of a calmodulin-1 promoter sequence that is damaged in human cortical samples from aged and young adult individuals. Note increased binding of parkin to chromatin from some aged cortical samples (≥ 73 years old) relative to young adult samples (<40 years old), which correlates with increased 8-oxoguanine content. Input and non-specific IgG ChIP controls are shown.