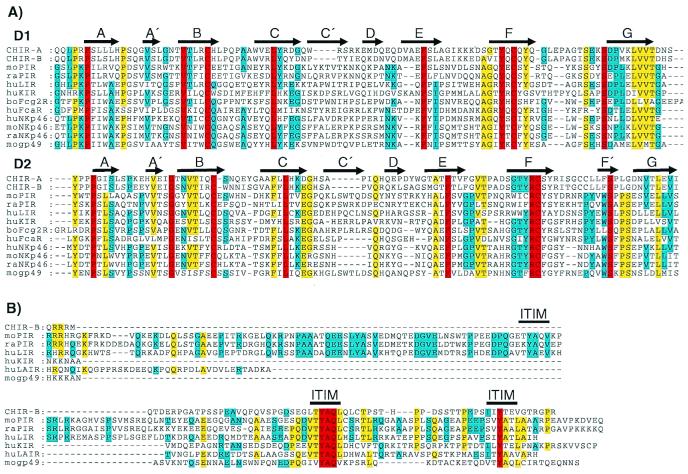
Figure 2.
(A) Sequence comparison of the two amino-terminal Ig-like domains of CHIR-A, CHIR-B, mouse (mo) PIR-B (AF038149), moNKp46 (AJ223765), mogp49-B (2997305), rat (ra) PIR-B (AF16936), raNKp46 (AF082533), human (hu) LIR-1 (AF009220), huKIR2DL1 (AF022049), huFcαR (U4774), huNKp46 (AJ001383), and bovine (bo) Fcγ2R (2136749). Gaps in the alignment are indicated by dashes, and bold arrows represent regions of β-stranded secondary structures (A–G) designated according to the crystal structure of human KIR (42). Residues identical in all of the aligned sequences are in red, yellow indicates 80% of the aligned sequences are identical, and blue indicates 60% identity for the aligned sequences. (B) Comparison of the CHIR-B, moPIR-B (AF038149), mogp49-B (2997305), raPIR-B (AF16936), huLIR-1 (AF009220), huKIR (AF022049), and huLAIR (AF013249) cytoplasmic tails, with gaps in this alignment indicated by dashes. Bold lines indicate moPIR-B ITIMs demonstrated to have inhibitory function. Red indicates residues that are identical in all of the aligned sequences, yellow indicates identity in 60% of the aligned sequences, and blue indicates 40% identity for the aligned sequences.