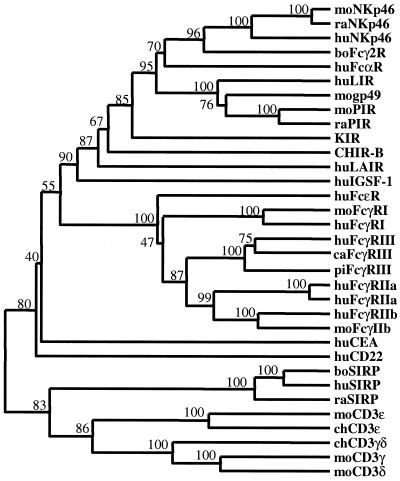
Figure 3.
Dendrogram of implied relationships among CHIR-like sequences identified in PSI-BLAST searches. Amino acid sequences for CHIR-B, moPIR-B (AF038149), moNKp46 (AJ223765), mogp49-B (2997305), moFcγRI (AF143180), moFcγRIIb (U31803), raPIR-B (AF16936), raNKp46 (AF082533), raSIRP (AAC18089), huLIR-1 (AF009220), huKIR2DL1 (AF022049), huFcαR (U4774), huNKp46 (AJ001383), huLAIR (AF013249), huFcɛRI (J03605), huFcγRI (L03418), huFcγRIII (AB032414), huFcγRIIa (M28697), huFcγRIIa′ (M31932), huFcγRIIb (U87564), huCD22 (S61375), huCEA (X16356), huSIRP (CAB46661), boFcγ2R (2136749), boSIRP (CAA71943), cat (ca) FcγRIII (AB025315), and pig (pi) FcγRIII (Q28942) were aligned using CLUSTALX and the Gonnet series substitution matrix. Human CD22 and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) were identified after the third iteration. Human, rat, and bovine SIRPs were not identified in the iterative searches but are included to provide a measure of tree topology (see text). Optimal tree topology was estimated by cluster analysis using the weighted pair-group method. Branch values represent percent bootstrap support after 500 replicates. The tree was rooted by the inclusion of mouse CD3ɛ (A31348), γ (CAA68667), and δ (CAA26198) and chicken CD3ɛ (Q98910) and γδ (A39171) as primordial Ig-like domains.