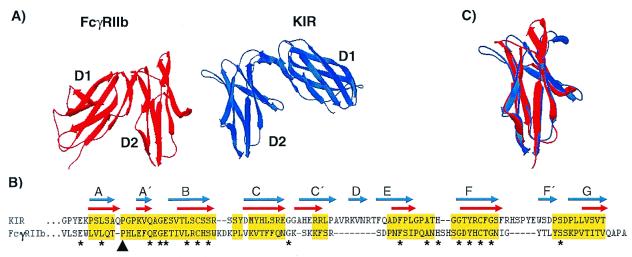
Figure 4.
(A) Crystal structures of the extracellular Ig-like domains of FcγRIIb (red) and KIR (blue). The second domains (D2) are placed in the same orientation to illustrate the relative difference in orientation between FcγRIIb D1 and KIR D1. (B) Structure-based alignment of FcγRIIb D2 and KIR D2. Gaps are indicated by dashes, and residues used in rms deviation calculations are highlighted in yellow. The β-stranded domain topologies are indicated for FcγRIIb by red arrows and for KIR by blue arrows. The black arrowhead indicates the cis-proline residue contributing to the A to A′-strand switch, and asterisks indicate identical residues in both sequences. (C) Structural overlay of FcγRIIb (red) and KIR (blue) D2 depicting their overall similarity. Structural decorations, alignments, overlays, and rms deviation calculations were performed using Swiss-pdb Viewer (30).