Figure 1.
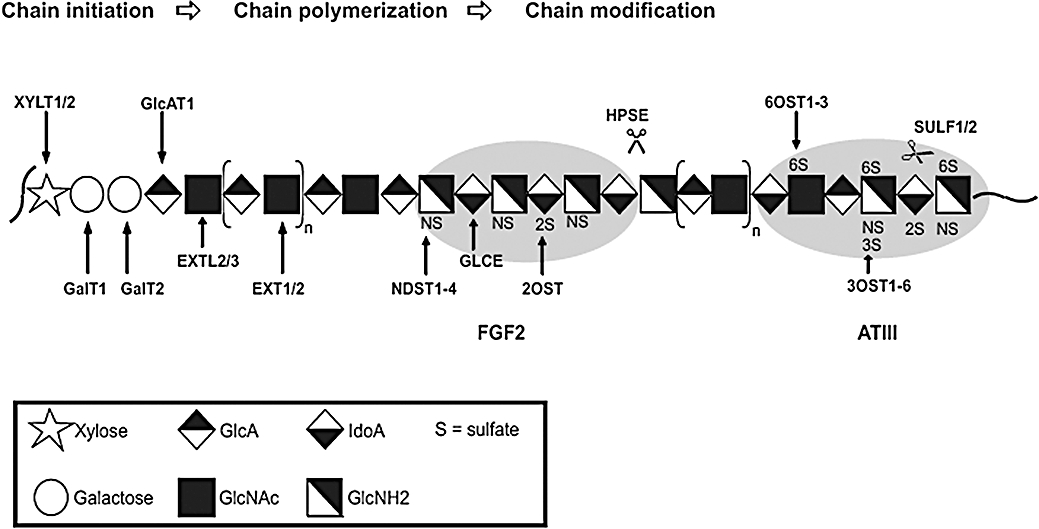
Scheme of HS-biosynthesis. Displayed is the consecutive action of the various biosynthetic enzymes durin chain initiation, polymerization and modification (the recently proposed model of a so-called GAGosome, in which the biosynthetic steps occur in a parallelized way (Ledin et al., 2006), has not been considered in this figure). Enzymes involved in HS biosynthesis are: XYLT1, xylosyltransferase-1; XYLT2, xylosyltransferase-2; GalT1, galactosyltransferase-1; GalT2, galactosyltransferase-2; GlcAT1, glucuronosyltransferase-1; EXT1, exostosin-1; EXT2, exostosin-2; EXTL2, exostosin-like-2; EXTL3, exostosin-like-3; NDST1-4, N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase-1, -2, -3, -4; GLCE, D-glucuronyl C5-epimerase; 2OST, 2-O-sulfotransferase; 3OST1-6, 3-O-sulfotransferase-1, -2, -3A, -3B, -4, -5, -6; 6OST1-3, 6-O-sulfotransferase-1, -2, -3; SULF1, extracellular sulfatase Sulf-1; SULF2, extracellular sulfatase Sulf-2; HPSE, heparanase. Two typical results of taylored HS biosynthesis are given in the form of the FGF2- and the ATIII-specific binding sites. HS, heparan sulphate.
