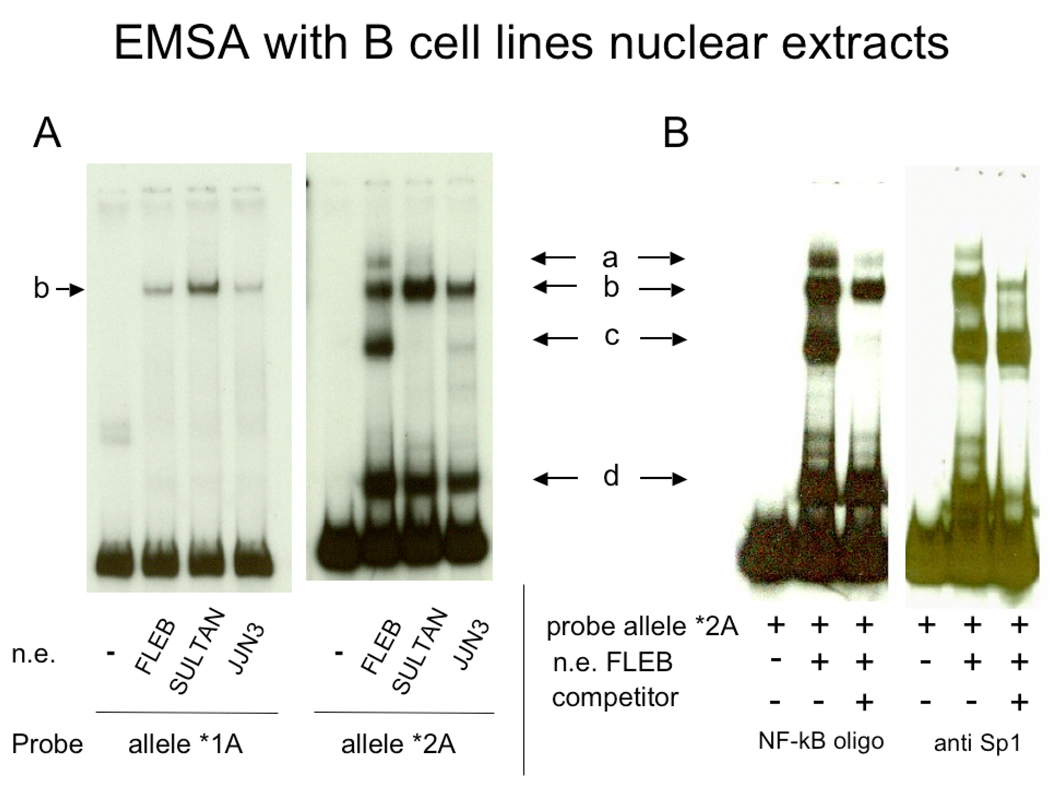
Figure 2.
EMSA of segments of HS1,2-A alleles *1 and *2 with nuclear extracts from different B cell lines. A) Two independent gel shift analyses in which alleles *1A and *2A were used as probes incubated with the nuclear extracts (NE) of FLEB human cell line (pro-B cells), Sultan human cell line (Burkitt lymphoma) and JJN3 human cell line (plasmacytoma cells) (see ref. 23). The binding patterns for the two alleles are clearly different. B) Identification of NF-κB and Sp1 binding sites in HS1,2*2A. EMSA with nuclear extracts from FLEB (pro-B cell line) was carried out with allele *2A as a probe together with an NF-κB consensus binding site or anti-SP1 antibody as competitors. SP1 antibodies eliminate bands b and d, while the NF-κB consensus competes for the binding of band c. The presence of a band in allele HS1,2 *1A of a similar mobility to band b of allele HS1,2 * 2A suggests that Sp1 similarly binds to both alleles. A slow mobility band (a) was occasionally detected.