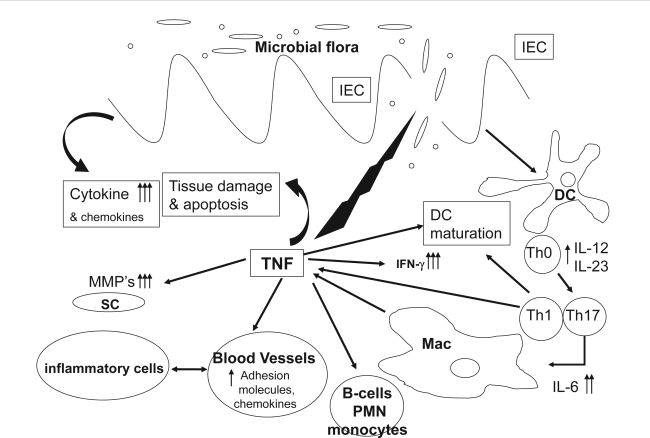
Figure 1.
TNF-α involvement in intestinal inflammation. After initial damage to the mucosal barrier, TNF-α is secreted by T lymphocytes, macrophages (Mac), and intestinal epithelial cells causing epithelial cell apoptosis, production of cytokines and chemokines, maturation of DCs and activation of tissue metaloproteinases from SC. This in turn causes further barrier damage, activation of neutrophils (PMN) and B lymphocytes, up-regulation of adhesion molecules, and further recruitment of inflammatory cells.
Abbreviations: IEC, intestinal epithelial cells; DC, dendritic cells; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; SC, stromal cells.