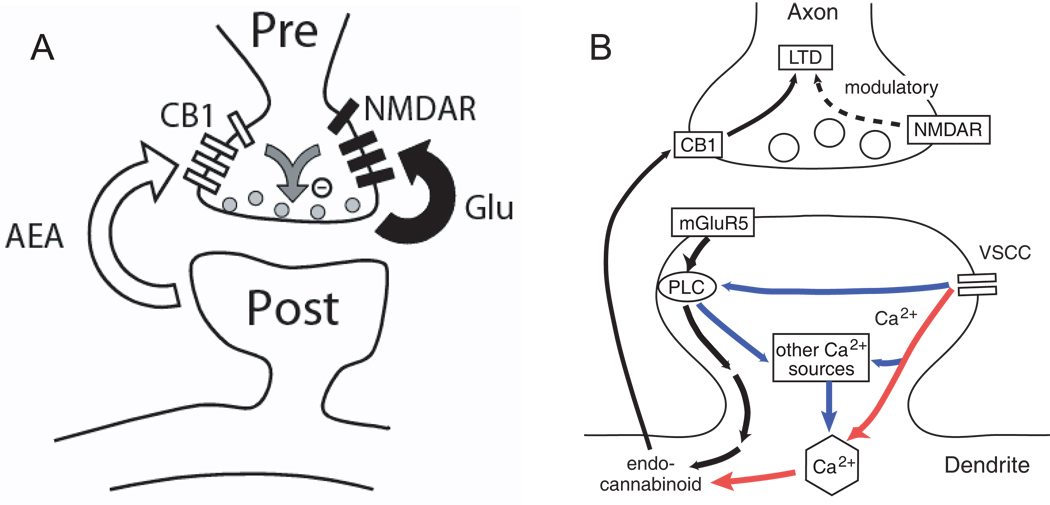
Fig. 6. Two models showing preNMDAR involvement in the coincidence detection of spike timing-dependent LTD.
(A) It has been proposed in L5 of visual cortex (Sjöström and others 2003) that postsynaptic action potentials trigger the release of endocannabinoids in a mechanism similar to short-term depression caused during depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition. When presynaptic activity follows this cannabinoid release in a short time window, it coincidently activates preNMDARs and presynaptic CB1 receptors to trigger LTD induction. Reproduced with permission from Sjöström and others 2003. (B) Schematic for a possible postsynaptic coincidence detector for CB1-mediated tLTD. Black, pathway for mGluR-dependent cannabinoid synthesis. Red, pathway for VSCC- and calcium-dependent cannabinoid synthesis. Purple, potential synergistic pathways that increase cannabinoid production in response to appropriately timed pre- and postsynaptic spikes. Presynaptic NMDARs play a modulatory role in LTD in this hypothesis. Schematic based on data in Bender and others 2006.