Fig. 1.
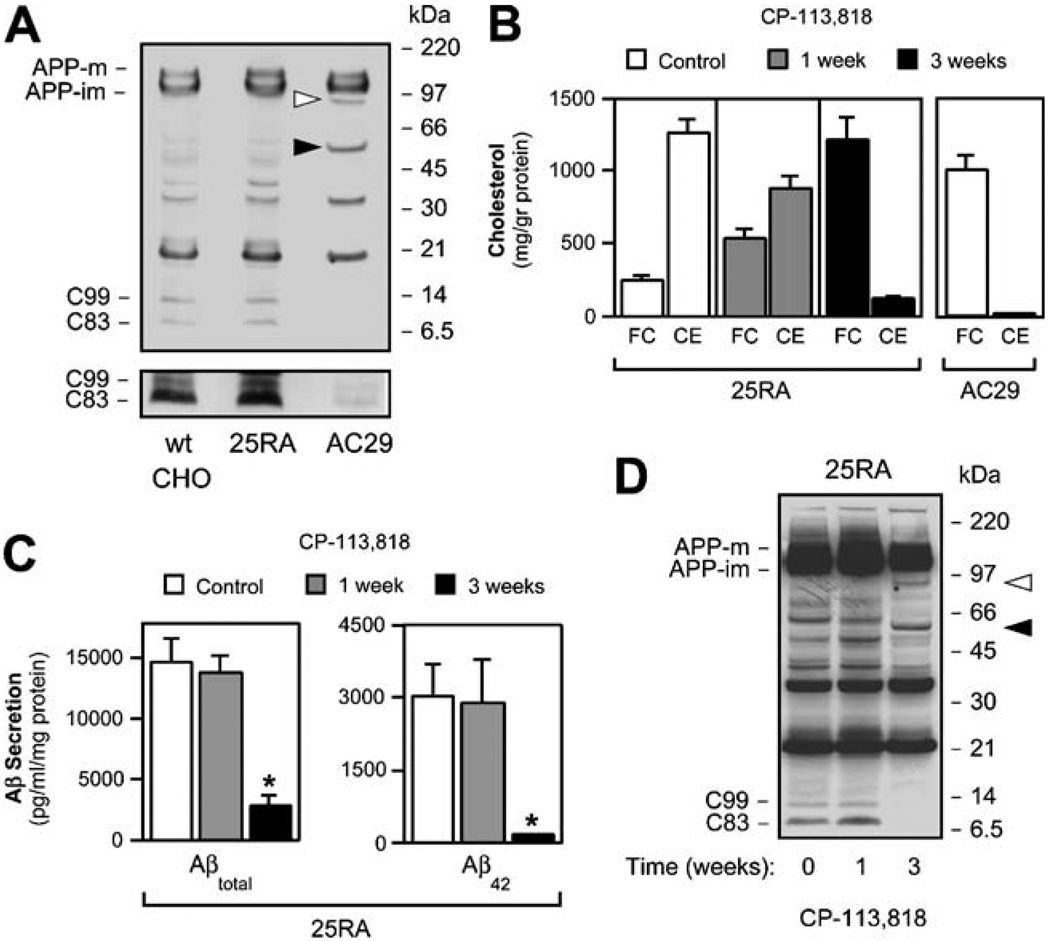
ACAT inhibition alters normal proteolytic processing of APP. a Western blot analysis of wild-type CHO, 25RA, and AC29 cell lines stably transfected with APP. Arrowheads indicate two novel APP-CTFs of ~85- and ~55-kDa, which are only visible in AC29 cells. The overexposed inset illustrates a marked reduction in C99 and C83 levels in AC29 cells. Antibody: C7, against the C-terminus of APP. b 25RA cells require 3 weeks of treatment with the ACAT inhibitor CP-113,818 (5 µM) to reach an FC-to-CE ratio similar to that found in AC29 cells. c The shift of cholesterol from the pool of CE to that of FC in 25RA cells almost completely abolished the secretion of both Aβtotal and Aβ42, as shown in a sandwich ELISA assay, and d was accompanied by the appearance of both ~55- and ~85-kDa APP-CTFs (arrowheads). A marked reduction in the steady-state levels of both C99 and C83 is also evident. Antibody: C7, against the C-terminus of APP. Values are the mean±SD of at least three independent experiments, asterisks, p<0.05