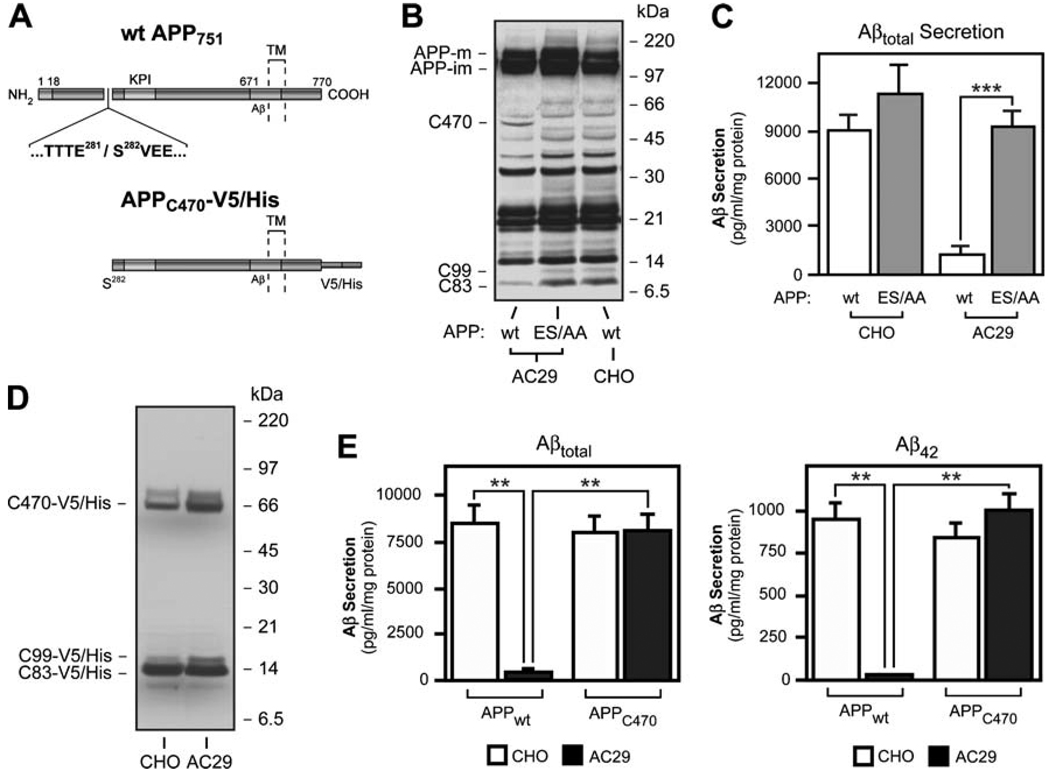
Fig. 4.
The 55-kDa APP-CTF is generated by cleavage of APP holoprotein at Glu281 and precludes α- and β-cleavages and Aβ generation in AC29 cells. a Schematic view of APP751 illustrating the site of Glu281 cleavage. The location of Aβ region and the Kunitz-type proteinase inhibitor (KPI) domain are indicated. The dotted lines indicate the single transmembrane (TM) region of APP. Below is a schematic view of APPC470-V5/His, an APP deletion mutant lacking the N-terminal 281 amino acids fused with a V5/His tag at the C-terminus. b Glu281 and Ser282 were mutagenized to alanine residues to abolish the generation of C470. Western blot analysis of AC29 cells stably transfected with the new construct, APP (ES/AA), shows that mutagenesis of the Glu281 cleavage site reactivated C99 and C83 production. Antibody: C7, against the C-terminus of APP. c AC29 cells stably transfected with APP (ES/AA) fully recovered their ability to generate and secrete Aβ into the media. Aβ levels in the media were detected by sandwich ELISA. d Western blot analysis showing that APPC470-V5/His is processed normally in AC29 cells, in terms of C83 and C99 production by α and β cleavages. Antibody: C7, against the C-terminus of APP. e AC29 cells stably expressing APPC470-V5/His recovered their ability to generate Aβ to normal levels, as shown by a sandwich ELISA. Values represent the mean±SD of at least three independent experiments. *,p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001