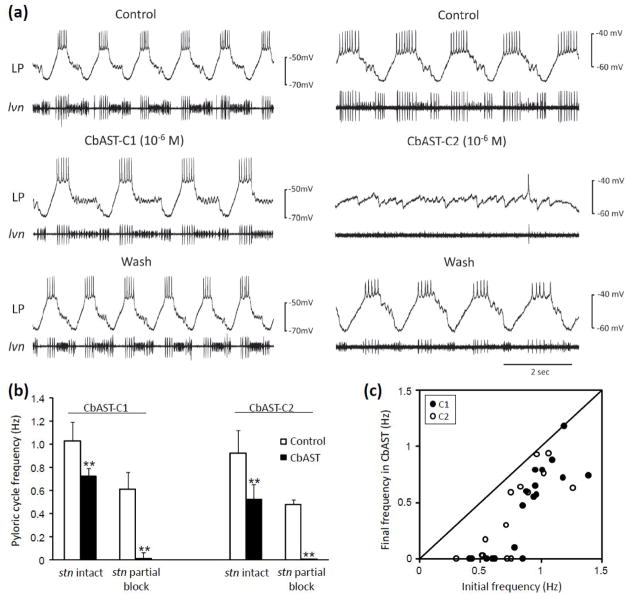
Figure 5.
Physiological effects of 10−6 M C-type CbASTs on the pyloric rhythm in the STG of the crab, C. borealis. (a) Effect of 10−6 M CbAST application on two preparations, one bursting more rapidly (left, ~1 Hz), and the other more slowly (right, ~ 0.5Hz). Each experiment shows representative intracellular recordings from the lateral pyloric (LP) neuron and extracellular recordings from the lateral ventricular nerve (lvn). The lvn contains axons from the lateral pyloric (LP), pyloric dilator (PD) and pyloric (PY) motor neurons, the activities of which together comprise a triphasic burst. (b) Summary of the effects of 10−6 M CbAST-C1 and 10−6 M CbAST-C2 on rhythmic activity on preparations with intact modulatory inputs, as compared to those with a partial blockade of modulatory inputs; **, p<0.0002. (c) Final pyloric frequency following application of 10−6 M CbAST-C1 or CbAST-C2 as a function of initial frequency for all preparations. Diagonal line represents the condition in which there was no difference between initial and final cycle frequencies following AST application for a given preparation.