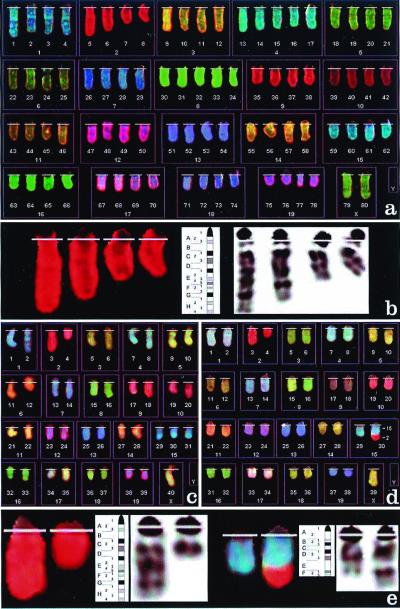
Figure 1.
(a) Spectral karyotype of a tetraploid cell from mouse 10759, containing an interstitial deletion of chromosome 2 as the only structural abnormality. (b) Localization of the chromosome 2 interstitial deletion from a. The comparison of chromosome's inverted 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole G-banding pattern and the G-banding ideogram for mouse chromosome 2 allows the identification of the deletion as del(2)(E2H1). (c) Spectral karyotype of a pseudodiploid tumor cell from mouse 11908, containing a deletion of chromosome 2 del(2)(Dter), an extra chromosome 15, and loss of the Y chromosome. (d) Spectral karyotype of a hypodiploid cell from mouse 10826, containing a translocation 2;15 as the only structural alteration, and loss of a sex chromosome. (e) Localization of the breakpoints of the deleted chromosome 2 and derivative 15 from d. Chromosome 2 (Left) is deleted at band 2D (as in c), and chromosome 15 (Right) at band 15E. The translocated fragment from chromosome 2 appears to span bands 2G through the terminus. Therefore, the abnormality is defined as translocation t(2;15) (G-ter;E) and most likely involves loss of chromosome 2 material containing bands 2E and 2F.