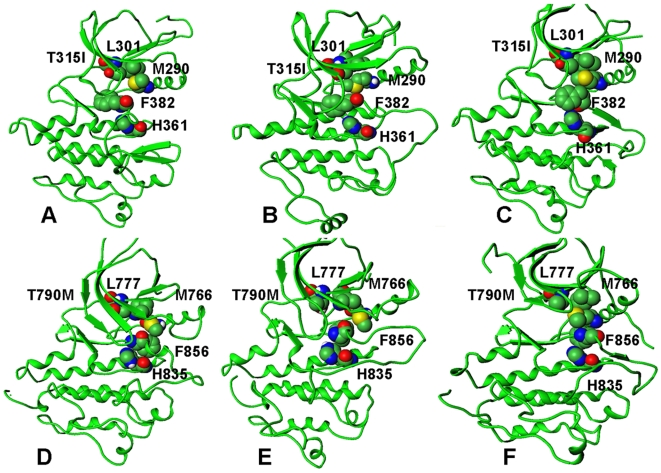
Figure 14. A mechanistic analysis of the TMD activation pathways for the ABL-L387M and EGFR-L858R mutations.
A dynamic assembly of the hydrophobic spine during TMD simulations is shown for the ABL-L387M mutant (upper panel) and the EGFR-L858R mutant (lower panel). (A) The initial model of ABL-L387M in the inactive form. (B) The characteristic TMD intermediate of ABL-L387M. (C) The final structure of ABL-L387M in the active form. (D) The initial model of EGFR-L858R in the inactive form. (B) The characteristic TMD intermediate of EGFR-L858R. (C) The final structure of EGFR-L858R in the active form. The assembled hydrophobic spine is present in all TMD intermediates.