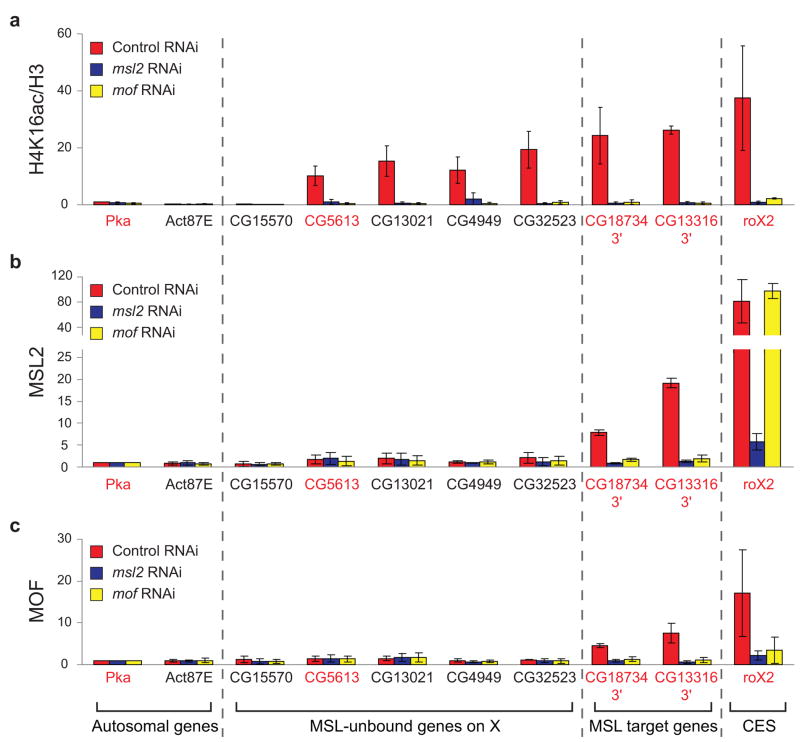
Figure 3.
MSL complex is required for broad H4K16ac on the male X. MSL2 and MOF are required for H4K16ac at sites on the X that lack detectable MSL binding. ChIP was performed following RNAi in SL2 cells for GFP as a negative control (red), msl2 (blue) or mof (yellow). Known MSL targets (3′ ends of MSL-bound genes and the roX2 CES (chromatin entry site)) and autosomal genes served as positive and negative controls, respectively. Five genes on the X that clearly lack detectable MSL binding11 were assayed. With the exception of CG15570, these genes were enriched by H4K16ac in SL2 ChIP-chip experiments, and primers were designed within the region of maximum ChIP signal. Genes were classified as transcribed (gene names in red) or untranscribed (gene names in black) based on Affymetrix analysis in SL2 cells5. H4K16ac ChIP signal (a) was quantified as percent IP normalized to input and H3 levels. The ChIP signals were normalized to the ChIP signal of the autosomal gene, Pka, in the control RNAi sample, and the replicates were averaged (see Supplementary Methods). Average MSL2 (b) and MOF (c) ChIP signals are presented as percent IP normalized to input and Pka levels. Error bars are defined as the standard deviation of three replicate experiments.