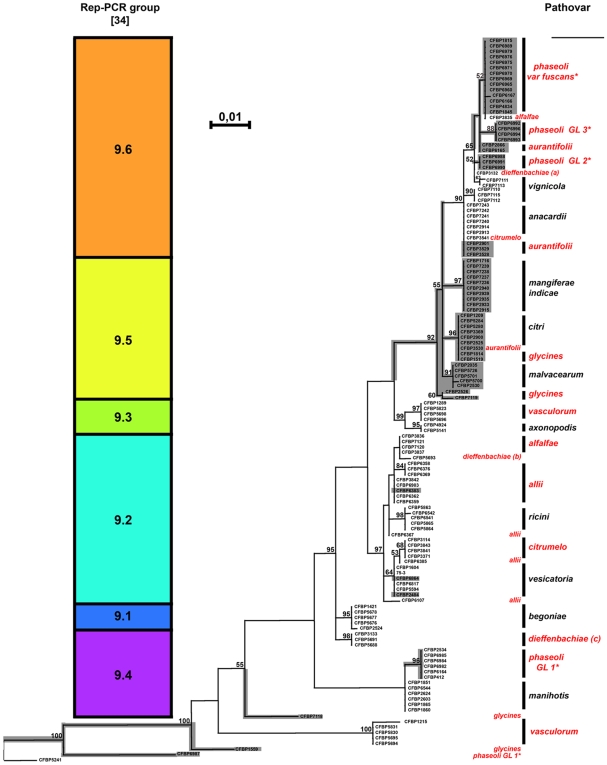
Figure 1. Phylogeny of 18 pathovars of Xanthomonas axonopodis based on rpoD gene sequences.
The phylogenetic tree was constructed using the method of maximum likelihood. Confidence on nodes was tested with 1000 bootstrap replicates. Bootstrap values under 50 are not reported. Bar, 0.01 substitution per site. The tree is rooted with the rpoD gene sequence of strain CFBP 5241 of Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris. The tree constructed based on rpoD sequences is congruent with previous grouping based on Rep-PCR profiles by Rademaker [34]. Polyphyletic pathovars are reported in red, whereas monophyletic are reported in black. *GL1, GL2, GL3, and var. fuscans correspond to the 4 genetic lineages previously described in the pv. phaseoli [24]. The dendrogram also displays the evolutionnary history of the T3E xac3090 as inferred from the parsimony method implemented in Mesquite [89]. Occurence of xac3090 is indicated on the tree by gray branches. For example, xac3090 is present in all the strains of pv. glycines. The parsimony analysis indicates that this T3E appeared several independent times in strains of X. axonopodis pv. glycines, as well as in other parts of the tree.