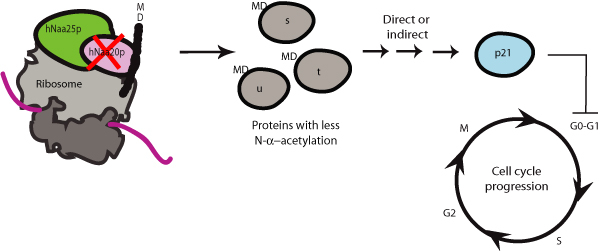
Figure 3.
Knockdown of hNAA20 of the hNatB complex leads to inhibition of growth and cell cycle arrest. Knockdown of hNAA20 may lead to reduced acetylation of hNaa20p substrates. As a direct or indirect effect of this, inhibition of cell growth, and G0-G1 cell cycle arrest is observed. The finding that p21 is upregulated after hNAA20 knockdown suggest a mechanism where loss of hNaa20p mediated acetylation leads to p21-mediated cell cycle arrest.