Figure 6.
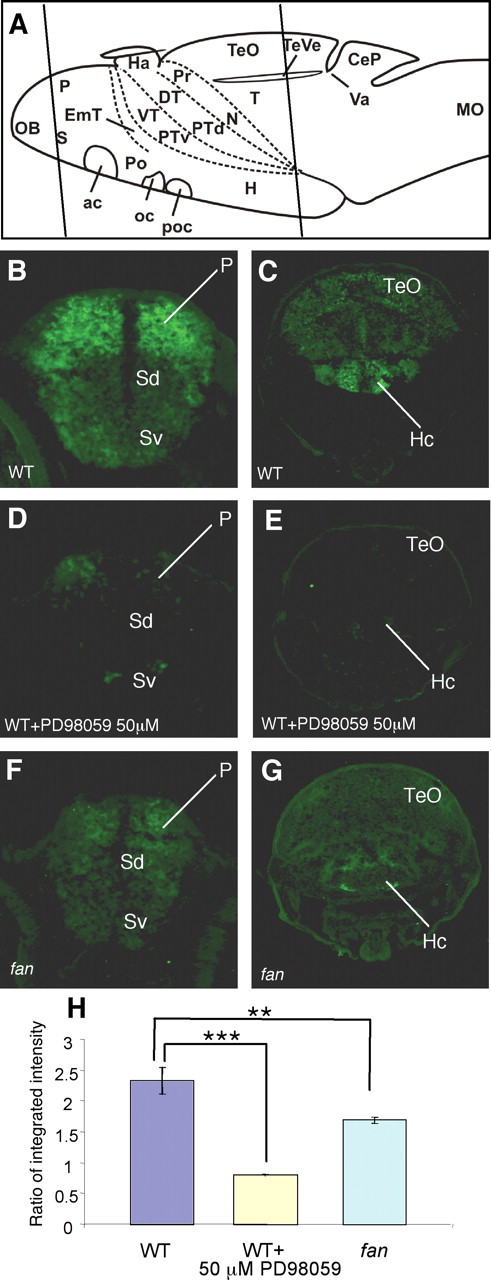
In the telencephalon and hypothalamus, fan/ac5 is required to maintain phosphorylation of ERK. A, Schemata showing anatomical regions of the larval zebrafish brain. Line 1 indicates sectioned regions shown in B, D, and F, and line 2 indicates sectioned regions shown in C, E, and G. B, C, Phospho-ERK immunoreactivity in the WT telencephalic (B) and hypothalamic (C) regions. Strong phospho-ERK staining is detected in the dorsal telencephalon (also know as the pallium) and the hypothalamus, whereas other brain regions show relatively low immunoreactivity. D, E, Phospho-ERK immunoreactivity in WT treated with 50 μm PD98059 for 1 h. Significant reduction of phospho-ERK staining is observed in both the pallium (D) and the hypothalamus (E) compared with untreated WT. F, G, Phospho-ERK immunoreactivity in the fan mutant telencephalic (F) and hypothalamic (G) regions, showing a significant reduction of immunoreactivity in both regions compared with a WT sibling. H, Quantification of immunofluorescence intensity in the pallial and hypothalamic regions in various conditions. The y-axis represents average ratio of integrated intensity between sectioned phospho-ERK and Hu immunostaining images. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005 (n = 15 brain sections from 3 animals in each assay condition). P, Pallium; SD, Dorsal division of subpallium; Sv, Ventral division of subpallium; TeO, tectum opticum; Hc, caudal hypothalamus.
