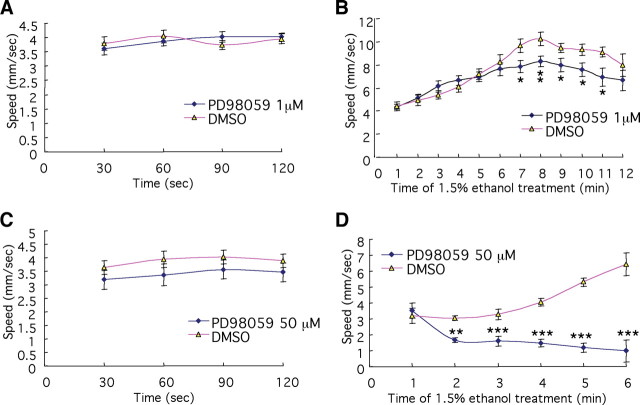
Figure 7.
Pharmacological inhibition of phosphorylation of ERK alters behavioral sensitivity to ethanol. A, C, Basal locomotor activity of PD98059-treated (blue lines) animals is not significantly different from control (red lines) (n = 15 for A, and n = 12 for C). B, Partial (1 μm PD98059) inhibition of phosphorylation of ERK reduces the locomotor stimulatory activity of 1.5% ethanol (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, n = 14 for each condition). D, Severe inhibition of ERK phosphorylation (with 50 μm PD98059) renders a normally stimulatory dose of ethanol sedating (**p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, n = 12 and 15 for PD98059-treated and DMSO-treated control, respectively).