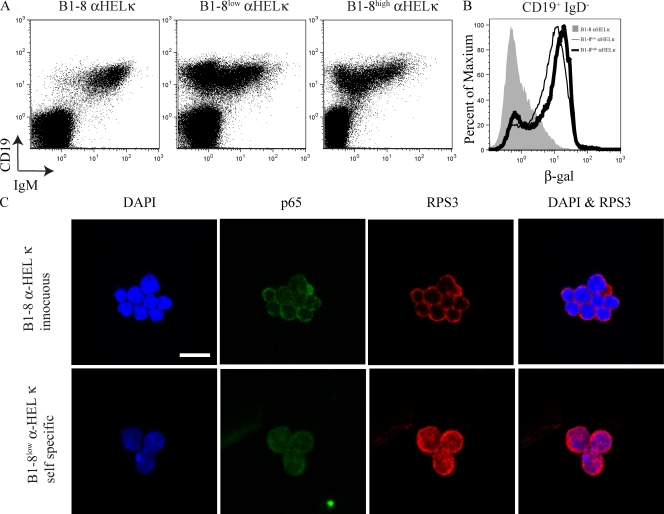
Figure 5.
Cells undergoing receptor editing show increased IκBα levels as well as increased nuclear NF-κB and RPS3. (A) Bone marrow was isolated from IκBα+/lacZ B1-8 α-HEL-κ, IκBα+/lacZB1-8high α-HEL-κ, and IκBα+/lacZB1-8low α-HEL-κ mice. Cells were loaded with FDG and stained with anti-CD19, anti-CD43, anti-IgM, and anti-IgD antibodies. Cells were first gated on IgD−. CD19 verses IgM staining is displayed. (B) β-gal activity in the CD19+IgD− gate (pro–B, pre–B, and immature B cells) is displayed. IκBα+/lacZ B1-8 α-HEL-κ is shaded gray, IκBα+/lacZB1-8low α-HEL-κ is the thin black line, and IκBα+/lacZB1-8high α-HEL-κ the thick black line. A and B are representative of at least three different mice individually analyzed for each genotype. (C) Immunofluorescence microscopy detecting p65 and RPS3 in B1-8 α-HEL-κ, B1-8low α-HEL-κ, and B1-8high α-HEL-κ pro–B, pre–B, and immature B cells. The data shown is representative of two independent sorts on each occasion scoring between 250 and 400 cells. Bar, 10 µm. Fig. S3 displays quantitative data from a repetition of this experiment.