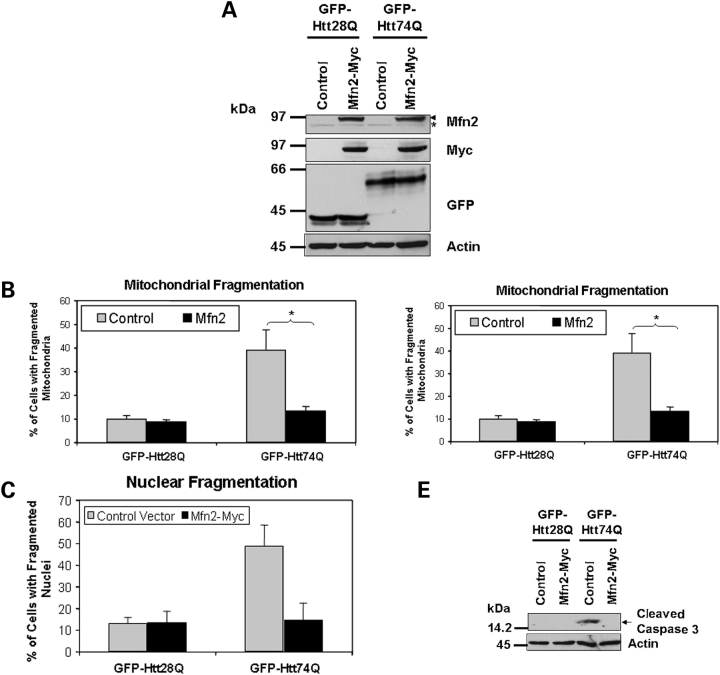
Figure 6.
Overexpression of Mfn2 reduces expanded polyglutamine-induced mitochondrial fragmentation and cell death. HeLa cells were co-transfected with either GFP-Htt28Q or GFP-Htt74Q expression constructs together with a Myc-tagged Mfn2 expression construct or an empty vector control plasmid. Twenty-four hours after the transfection, cells were fixed and immunostained with either the anti-Tom20 antibody or Hoechst. Additionally, protein lysates were prepared from the transfected cells and analyzed for expression of various proteins by immunoblotting. Mitochondrial fragmentation and cell death was quantified by counting a minimum of 650 GFP-Htt28Q and GFP-Htt74Q-expressing cells. (A) Immunoblots showing the expression of Myc-tagged Mfn2, and GFP-tagged Htt28Q and Htt74Q proteins probed with an anti-Mfn2 antibody (upper panel, arrow head indicates Myc-tagged Mfn2 and the asterisk, endogenous Mfn2) an anti-myc antibody (second panel) and anti-GFP antibody (third panel). The actin blot (lower panel) serves to demonstrate equal protein loading. (B) Overexpression of Mfn2 reduces GFP-HttQ74-induced mitochondrial fragmentation. Cells with or without fragmented mitochondria (see Materials and Methods) were counted using a fluorescence microscope using a 100× oil objective lens. The resulting data is presented as the percentage of cells with fragmented mitochondria of the total GFP expressing cells (*P < 0.01). (C) Overexpression of Mfn2 alleviates the GFP-Htt74Q-induced reduction of ATP levels in cells (*P < 0.05). (D) Overexpression of Mfn2 reduces GFP-Htt74Q-induced nuclear fragmentation (*P < 0.001). (E) Overexpression of Mfn2 inhibits GFP-Htt74Q-induced caspase-3 activation. The data in all the graphs shown are the mean ± SDM.