Figure 7.
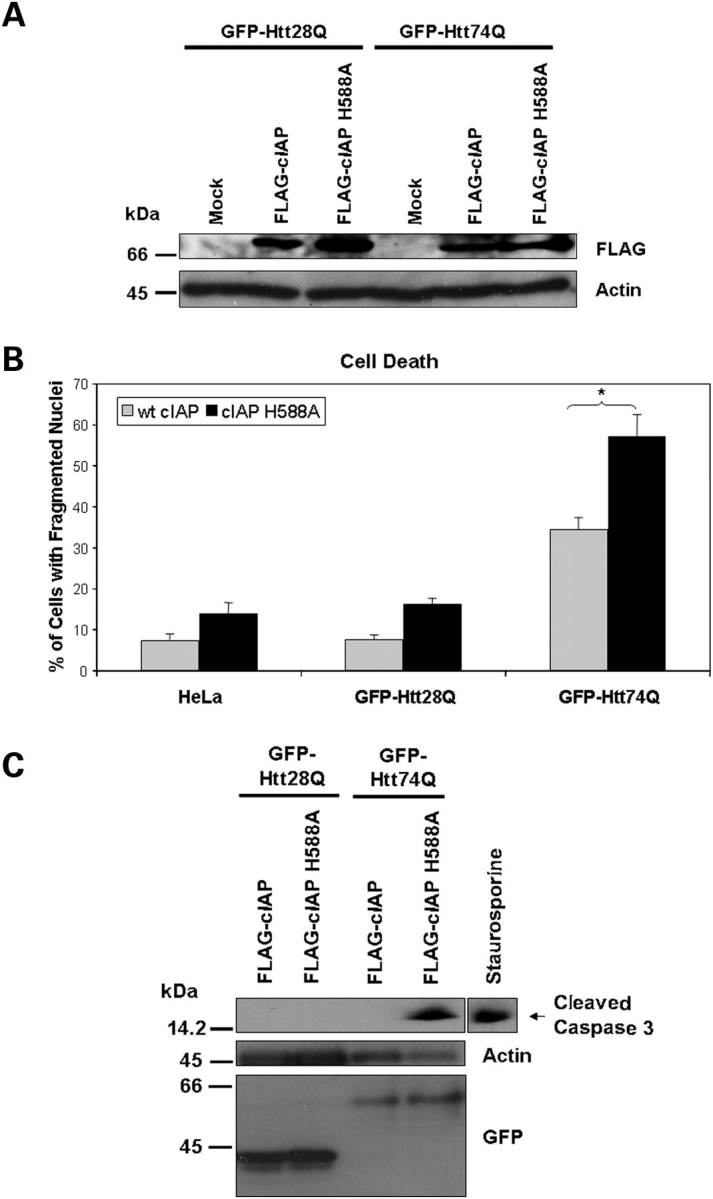
Overexpression of wild-type c-IAP but not a c-IAP H588A RING mutant suppresses expanded polyglutamine induced caspase-3 activation and cell death. GFP-28Q and GFP-74Q stable expressing HeLa cell lines were either mock transfected or transfected with either a FLAG-tagged wild-type c-IAP or a c-IAP H588A RING-finger ubiquitin ligase mutant. Following transfection, the cells were cultured in medium containing low serum (1.25% FBS) and cell death was quantified after staining with Hoechst, or alternatively protein lysates were prepared and immunoblotted for expression of the FLAG-tagged constructs or for caspase-3 activation. (A) Immunoblot of protein lystates showing expression of the FLAG-tagged c-IAP constructs (upper panel) and actin (lower panel) used as a loading control. (B) Expression of wt FLAG-tagged c-IAP reduces oxidative stress-induced cell death in GFP-Htt28Q and GFP-Htt74Q-expressing lines compared with the expression of the c-IAP-H588A mutant. The data shown are the quantification of fragmented nuclei in the parental HeLa cell line (HeLa) and the two daughter GFP-Htt28Q and GFP-Htt74Q-expressing cell lines. At least 500 cells were counted for these quantifications. Mean ± SEM (*P < 0.001). (C) Overexpression of wt FLAG-tagged c-IAP, but not the c-IAP H588A mutant inhibits oxidative stress-induced caspase-3 activation in the GFP-Htt74-expressing cell line. A HeLa cell lysate from a staurosporine treated culture (right lane) was used as a positive control to detect the caspase-3-cleaved fragment.
