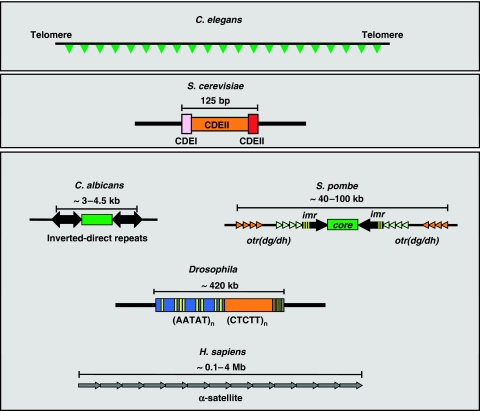
Figure 1.
Structural organisation of the different classes of eukaryotic centromeres. In holocentric organisms (C. elegans), centromeres form along the entire chromosome. Most eukaryotes, however, contain monocentric chromosomes, in which the centromere forms at a single, generally large, chromosomal region (C. albicans, S. pombe, Drosophila, H. sapiens). In S. cerevisiae, centromeric function resides in a small 125 bp long conserved DNA sequence. See text for details.