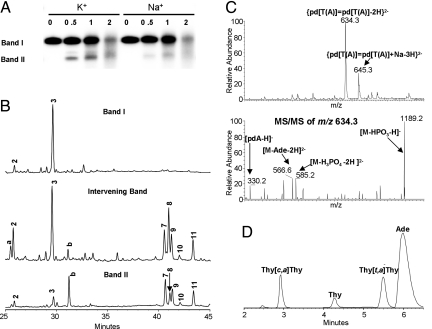
Fig. 3.
Analysis of UVB irradiated telomeric quadruplexes. (A) Tel22 was UVB irradiated in 150 mM Na+ or K+ solution at pH 7.5 for the number of hours indicated in the lane headings, 32P-end-labeled, and then subjected to 15% denaturing PAGE. Bands I and II and the intervening band were excised and subjected to NP1 digestion. (B) NP1-coupled HPLC assay of nonradiolabeled samples corresponding to bands I, II, and the intervening band. HPLC peaks a and b were not observed in nonelectrophoresed samples and could not be assigned. Products were detected at 260 nm where the nondimerized bases have their maximum absorption. (C) Mass spectra and product-ion mass spectra of the major nonadjacent photoproduct HPLC peak 8. The observation of [pdA − H]− and [M − Ade − 2H]2− indicate that adenine is the nonphotodimerized base. (D) HPLC assay of HF/pyridine hydrolysis products of HPLC peak 8 that was contaminated with adjacent peaks. The hydrolysis products were detected at 205 nm where the photodimers have their maximum absorbance, and their stereochemistry assigned by correlation with authentic thymine photodimers (Fig. S2B). The small thymine peak may be caused by the decomposition of thymine anti dimers in the course of hydrolysis (17). Analysis of various HPLC fractions established peak 8 to be the trans,anti photodimer.