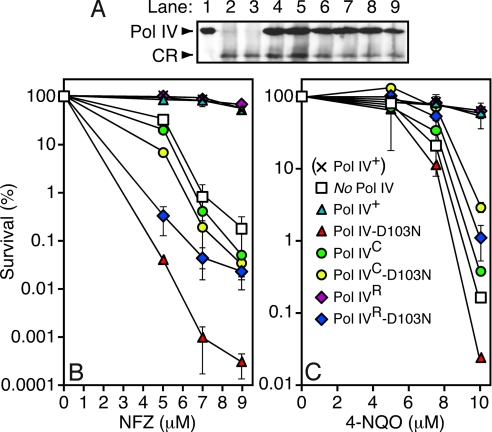
Fig. 4.
Ability of various mutant dinB alleles to complement NFZ and 4-NQO sensitivity of a ΔdinB E. coli strain. (A) Steady state levels of the indicated Pol IV proteins were measured by western blotting of whole cell extracts of strain JH100 (relevant genotype, ΔdinBW2::cat) bearing the indicated plasmid using a polyclonal anti-Pol IV antibody (25) and chemilumenescent detection (Pierce). Lane 1, purified Pol IV (5 ng); lane 2, no plasmid; lane 3, (pWSK29; empty vector control); lane 4, (pRM102; Pol IV+); lane 5, (pJH100; Pol IV-D103N); lane 6, (pJH101; Pol IVR); lane 7, (pJH102; Pol IVC); lane 8, (pJH103; Pol IVR-D103N); lane 9, (pJH104; Pol IVC-D103N). CR refers to a polypeptide which cross reacts with the anti-Pol IV antibody, and serves as a loading control. Sensitivity of strain AB1157 (× Pol IV+), or JH100 bearing the specified Pol IV-expressing plasmid (see legend in panel C), to the indicated concentration of NFZ (B) or 4-NQO (C) is shown. Results represent the average of 2 independent experiments, each performed with an independent transformant. Error bars represent the range.