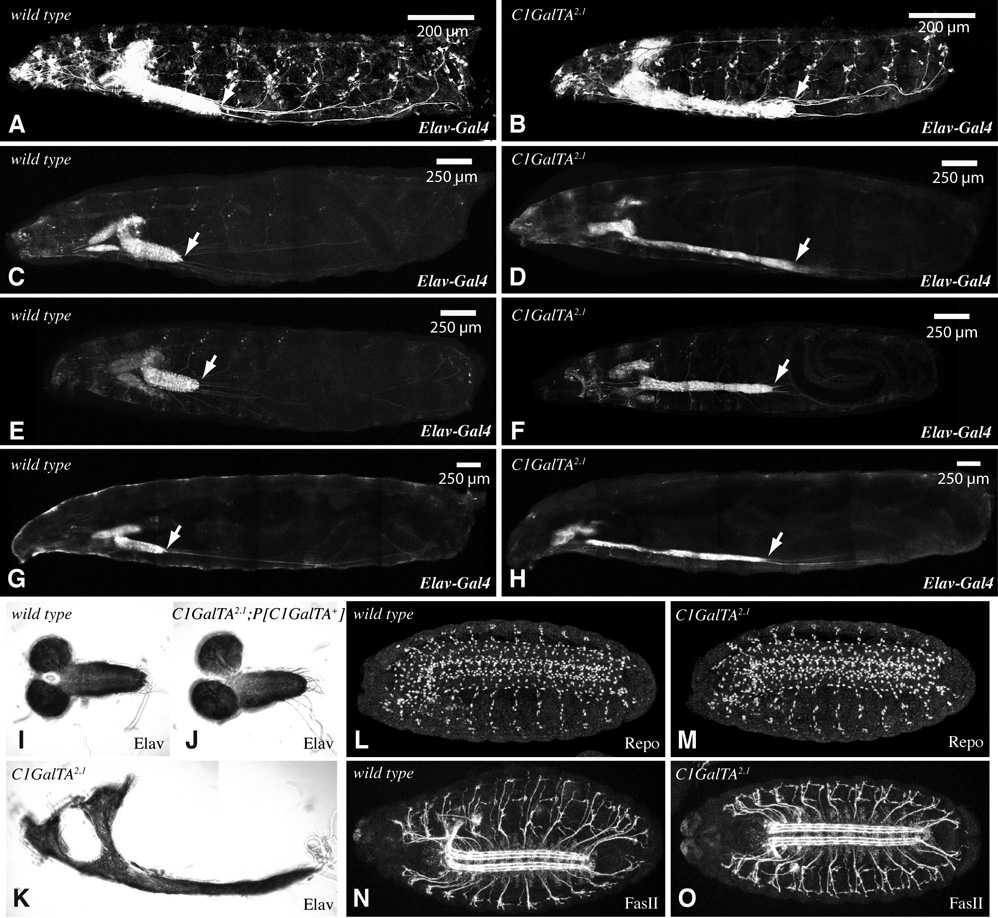
Figure 6. VNC Phenotype of C1GalTA mutants.
A–H) Composite confocal images of larvae with Elav-Gal4 and UAS-GFP transgenes. GFP is expressed in the nervous system and salivary glands, arrow points to the posterior end of the VNC. A–D, G, H are saggital views, E,F is a ventral view. A) wild-type first instar. B) C1GalTA2.1 mutant first instar. C) wild-type second instar. D) C1GalTA2.1 mutant second instar. E) wild-type second instar. F) C1GalTA2.1 mutant second instar. G) wild-type third instar. H) C1GalTA2.1 mutant third instar. I) Dissected late third instar CNS from wild type, stained with anti-Elav. J) Dissected late third instar CNS from C1GalTA2.1 mutant with P[C1GalTA+] rescue construct, stained with anti-Elav. K) Dissected late third instar CNS from C1GalTA2.1 mutant, stained with anti-Elav. L,M) Stage 16 wild-type (L) and C1GalTA2.1 mutant (M) embryos stained with anti-Repo to detect glial cells. N,O) Stage 16 wild-type (N) and C1GalTA2.1 mutant (O) embryos stained with anti-FasII to detect a subset of axon fasicles.