Fig. 1.
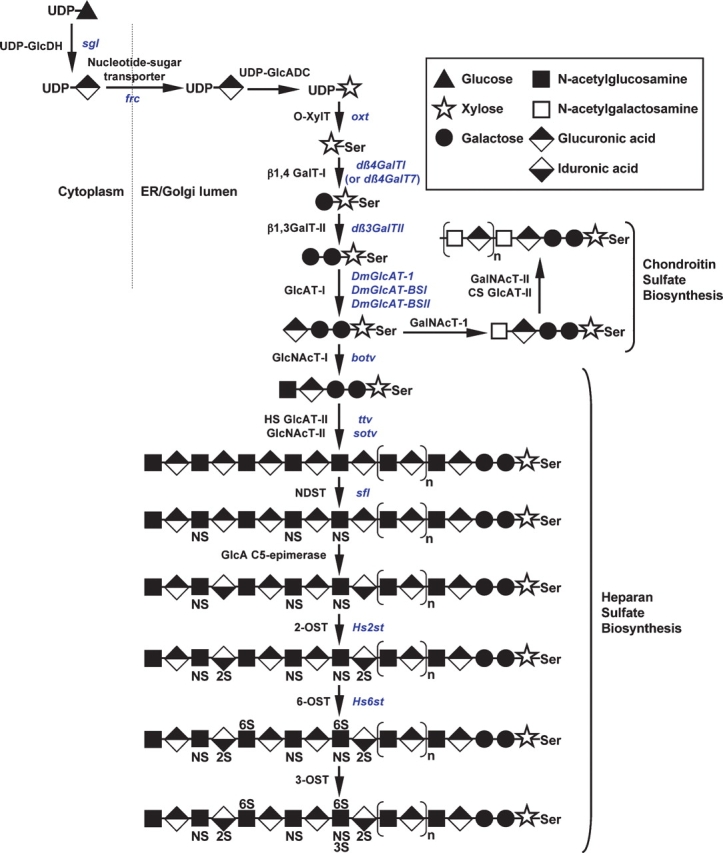
Biosynthesis of glycosaminoglycans. The initiation of chondroitin sulfate (CS) and the complete synthesis of heparan sulfate (HS) are shown. Enzymes responsible for catalyzing each step are shown in black and the corresponding Drosophila genes are shown in blue. Enzyme abbreviations are as follows: UDP-GlcDH, UDP-glucose dehydrogenase; UDP-GlcADC, UDP-glucuronic acid decarboxylase; O-XylT, polypeptide O-xylosyltransferase; β1,4GalT-I, xylose-β1,4-galactosyltransferase; β1,3GalT-II, galactose-β1,3-galactosyltransferase; GlcAT-I, galactose-β1,3-glucuronyltransferase; GalNAcT-I, glucuronic acid-β1,4-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase; CS GlcAT-II, chondroitin sulfate GalNAc-β1,3-glucuronyltransferase; GalNAcT-II, glucuronic acid-β1, 4-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase; GlcNAcT-I, glucuronic acid-α1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase; HS GlcAT-II, heparan sulfate GlcNAc-β1, 4-glucuronyltransferase; GlcNAcT-II, glucuronic acid α1,4-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase; NDST, N-deacetylase/N-sulfotransferase; 2-OST, 2-O-sulfotransferase; 6-OST, 6-O-sulfotransferase; 3-OST, 3-O-sulfotransferase.
