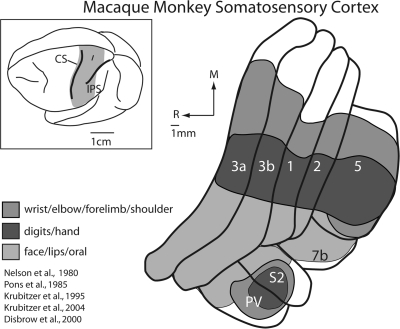
Figure 1.
Somatosensory cortical areas in macaque monkeys. The shaded region in the top left illustration of the entire brain indicates the location of somatosensory cortical areas in macaque monkeys shown in the illustration to the right. These include area 3b, which is buried in the caudal bank of the central sulcus and area 3a, which is on the fundus and rostral bank of the central sulcus, although the position of area 3a can vary in different monkeys. Other somatosensory areas in anterior parietal cortex include areas 1 and 2, which reside on the postcentral gyrus. Area 5 is a posterior parietal field located on the rostral bank of the IPS, and areas S2 and the parietal ventral area (PV) are located on the upper bank of the lateral sulcus. Area 7b is also associated with somatosensory processing. The extent of the neocortex occupied by different body part representations within each of the cortical fields is indicated in a different color. Portions of the cortex devoted to the representations of the forelimb are shown in medium grey, portions of the cortex devoted to the representation of the hand and digits are indicated in dark grey, and portions of the cortex devoted to the representation of the face, lips and oral structures are indicated in light grey. There are 2 important features of organization of somatosensory areas. The first is that the representation of the face, hand and forelimb dominates all these fields. Second, at higher processing stages such as posterior parietal area 5, the cortical magnification of the hand and forelimb is further exaggerated, with only a small portion of the field devoted to other body part representations. See Table 1 for abbreviations.