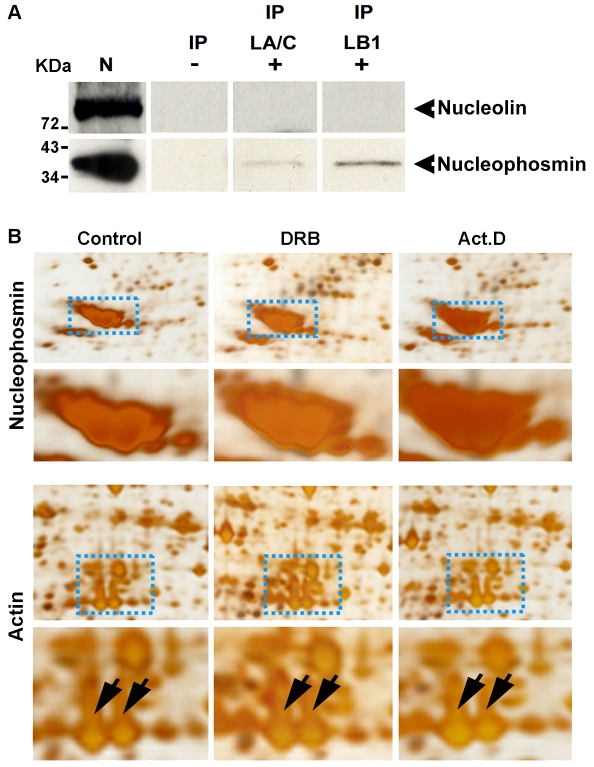
Fig. 6.
Lamin B1 preferentially associates with nucleophosmin within the nucleolar compartment. HeLa cells were processed for IP and protein complexes linked to lamin B1 or lamin A/C were separated by electrophoresis. Two major GC proteins (nucleolin and nucleophosmin) were then detected by immunoblotting (A). In three separate experiments, nucleophosmin showed a clear association with the nuclear lamin IP fractions, particularly lamin B1 (exposure 40 minutes). No detectable signal was seen when immunoblotting was performed using antibodies to nucleolin (A). IP, IP fraction with either lamin A/C (LA/C) or lamin B1 (LB1); N, nuclear extract (positive control for blotting); (–), IgG (negative control for IP). (B) Proteins from nucleoli isolated after drug treatment to inhibit RNA polymerase I (Act. D) or II (DRB) were inspected after separation by 2D gel electrophoresis. The intensity of the major nucleolar protein nucleophosmin (upper panel, enlargement below) increased by ∼1.5-fold after DRB and by ∼2.5-fold after Act. D treatment. As a loading control, actin spots from the same gels do not show any intensity variations (lower panel, actin indicated by the arrows on the corresponding enlargement). Images shown are representative of typical gels from experiments performed on at least three occasions.