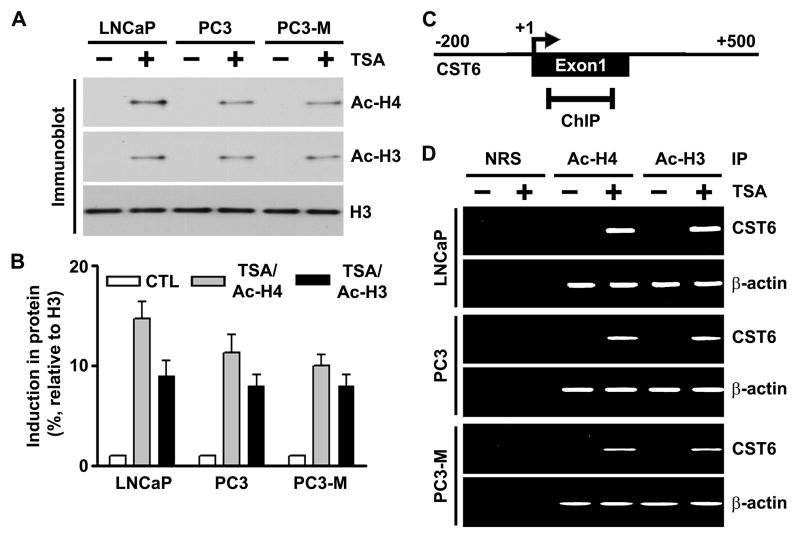
Figure 3. TSA induces accumulation of acetylated histones H3 and H4 in chromatin associated with the CST6 gene.
(A) Nuclear extracts were isolated from control and TSA-treated LNCaP, PC3 and PC3-M cells, and immunoblot analysis was performed using anti-acetyl histone H3, anti-acetyl histone H4, and histone H3 antibodies. Histone H3 was utilized as a loading control.
(B) Densitometric analysis of immunoblots in (A) from control and TSA-treated cell lines. Data are normalized to H3, averaged, and expressed as percentage of control (CTL=1).
(C) Schematic representation of the CST6 promoter region and the location of primers used for PCR amplification in the ChIP assay. Bent arrow, transcriptional start site (+).
(D) Chromatin fragments from LNCaP, PC3 and PC3-M cells cultured with (+) or without (−) TSA for 20 h were immunoprecipitated with antibody to acetylated (Ac) histones H3 and H4 or control normal rabbit serum (NRS). PCR primers for the CST6 and β-actin promoters were used to amplify the DNA isolated from the immunoprecipitated chromatin as described in Materials and Methods. Note the CST6 promoter specific primers amplified PCR fragment of 157-bp.