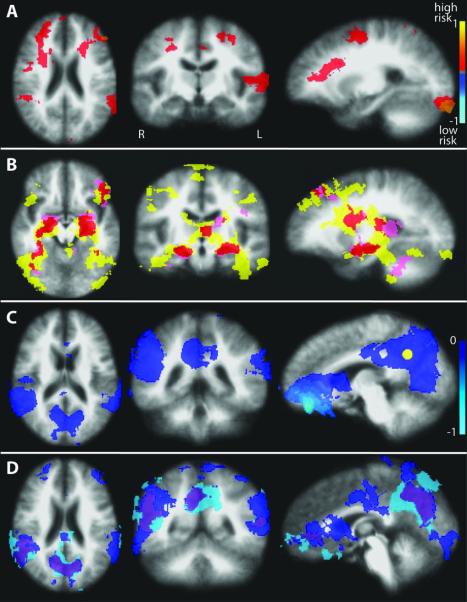
Figure 1.
Encoding-associated BOLD signal change. Anatomical image is an average of all 29 subjects. A) Between group differences in encoding-associated percent BOLD signal change from voxel-wise t-tests, showing multiple areas of increased signal in the high risk group compared to the low risk group. B) Regions of encoding-associated increased BOLD signal for each risk group based on within-group t-tests, overlapped on to a single map: yellow = high risk (n=17), pink = low risk (n=12), red = areas of overlapping activations for the low and high risk groups. C) Significant encoding-associated deactivations in the entire cohort (n=29) representing the default mode network. The yellow sphere represents the pC/rsp seed placement for the subsequent resting DMN correlation analysis (Figure 3). D) Regions of encoding-associated decreased BOLD signal for each risk group based on within-group t-tests, overlapped on to a single map: light blue = high risk, dark blue = low risk, purple = areas of overlapping deactivations for the low and high risk groups.