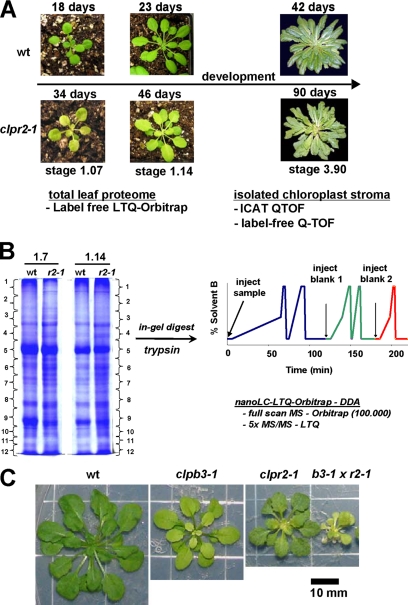
Fig. 1.
Comparative proteome analysis of wt and clpr2-1 and CLPB3 mutant analysis. A, outline of the comparative proteome analysis of clpr2-1 and wt. Total leaves were harvested at growth stages 1.07 and 1.14 at, respectively, 18 and 23 days for wt and 34 and 46 days for clpr2-1 for the comparison of total cellular proteomes. Soluble stromal proteins were collected from chloroplasts isolated from fully developed wt and clpr2-1 plants at growth stage 3.90 at 42 and 90 days, respectively, for wt and clpr2-1. The seedling proteomes were compared using the spectral counting technique from data obtained by nano-LC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap, whereas the stromal proteomes were compared using spectral counting and ICAT using data obtained by nano-LC-ESI-Q-TOF. B, example of 1-D electrophoresis gels of extracted seedling proteomes at stage 1.07 and stage 1.14. Gels were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue, and each lane was cut in 12 slices followed by manual in-gel digestion and extraction of peptides. Samples were analyzed in duplicate on the LC-LTQ-Orbitrap following the gradient and injection scheme as depicted. Two blanks were injected after each sample to prevent carryover between samples. C, comparison of the wt, clpr2-1, clpb3-1, and clpb3-1xclpr2-1 (b3-1 x r2-1) mutants grown on Murashige and Skoog medium + 2% sucrose for 10 weeks under a 10-h light/14-h dark cycle at 60 μmol photons·m−2·s−1. DDA, data-dependent acquisition.