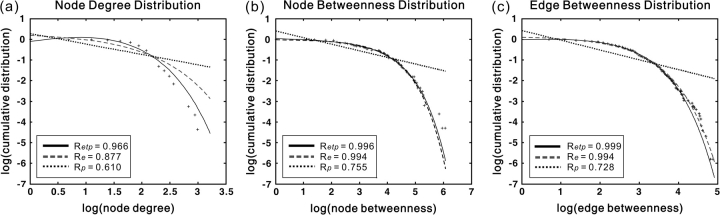
Figure 7.
The degree and betweenness distributions of the human cortical network. (a) Log-log plot of the cumulative node degree distribution; (b) log-log plot of the cumulative node-betweenness distribution; (c) log-log plot of the cumulative edge-betweenness distribution. The plus sign represents observed data, the solid line is the fit of the exponentially truncated power-law (p(x) ∼ xα−1exp(x/xc)), the dashed line is an exponential (p(x) ∼ exp(x/xc)), and the dotted line is a power-law (p(x) ∼ xα−1). R2 was calculated to assess the goodness-of-fit (a larger value indicates a better fitting; Retp, R2 for exponentially truncated power-law fit; Re, R2 for exponential fit; Rp, R2 for power-law fit). The exponentially truncated power-law is the best fitting for all the 3 distributions (a, estimated exponent α = 1.66 and cutoff degree kcnode = 3.65; b, estimated exponent α = 0.96 and cutoff betweenness Bcnode = 76.93; c, estimated exponent α = 1.10 and cutoff betweenness Bcedge = 18.95).