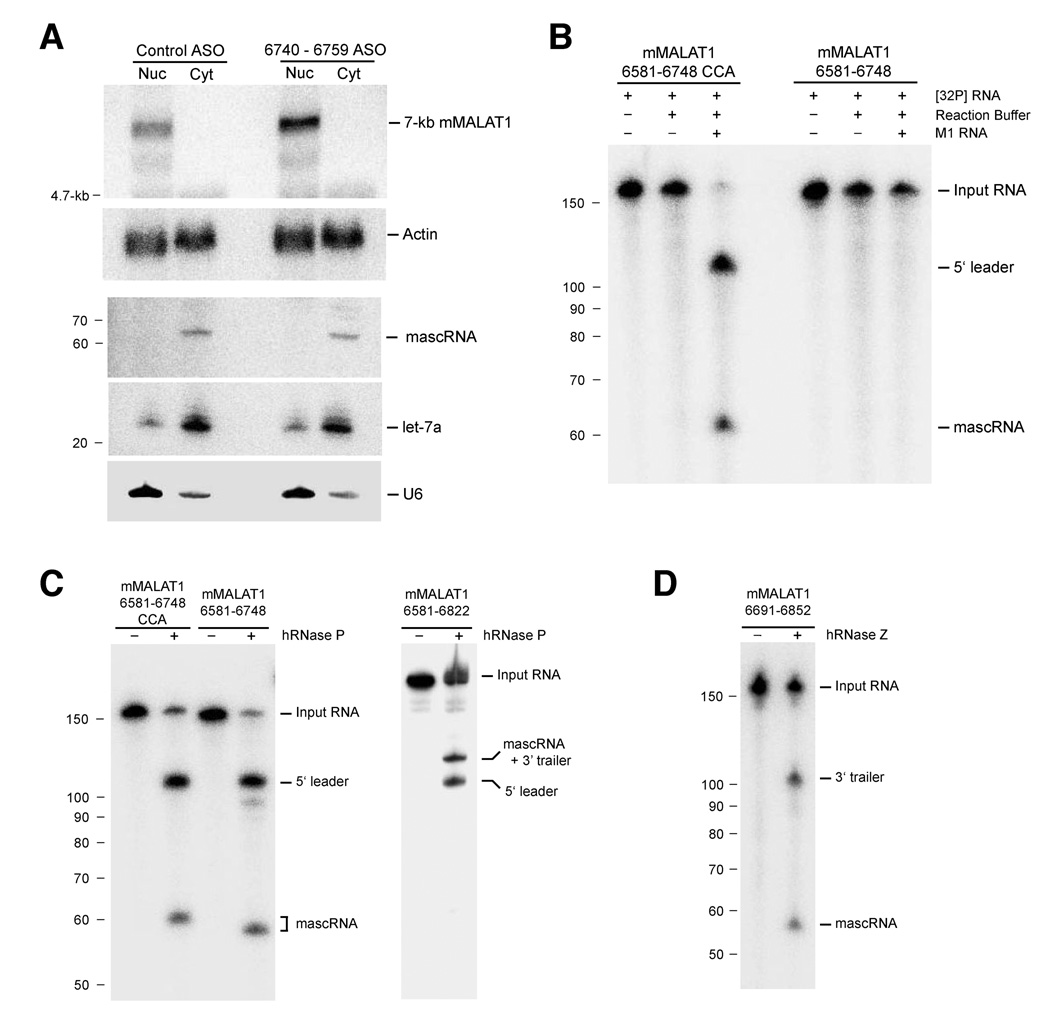
Figure 6. RNase P and RNase Z cleave MALAT1 in the nucleus to yield the mascRNA transcript.
(A) After ASO transfection, EpH4-EV cells were fractionated to isolate nuclear and cytoplasmic total RNA. The ~7-kb mMALAT1 transcript was nuclear-retained and ASO treatment did not affect the cytoplasmic localization of mascRNA. U6 and let-7a were used as controls for fractionation efficiency. (B) MALAT1 can be cleaved in vitro by E. coli RNase P. M1 RNA from E. coli was incubated for 1 hr at 37 degrees with uniformly labeled MALAT1 substrates. Samples were then electrophoresed in a 8% polyacrylamide/8 M urea gel. (C) MALAT1 can be cleaved in vitro by partially purified human RNase P. (D) Recombinant His-tagged human RNase Z cleaves MALAT1 in vitro at the 3’ end of mascRNA.