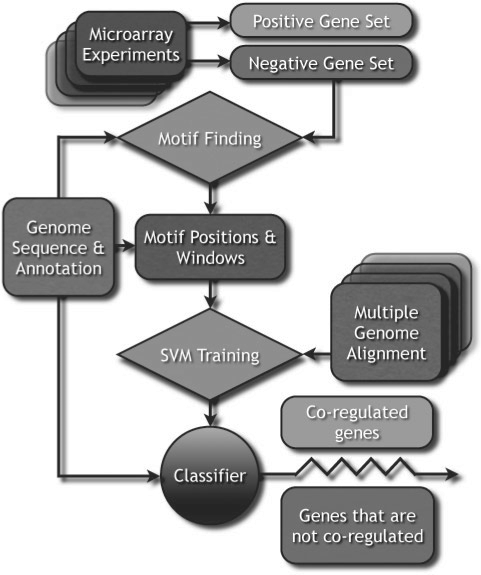
Fig. 2.
A cartoon workflow of the kirmes pipeline: the preprocessing step requires the genomic sequence and a set of regulatory sequences from genes that were determined to be co-expressed in microarray experiments, and ideally a negative set. kirmes conducts a motif finding step, where it locates the positions of overrepresented motifs in fasta files of the genes' regulatory region. For the classification, we build an input vector with sequence sections of 20 bp, centered around the motif positions obtained during the motif finding step, and optional conservation information from related genome sequences for the WDSC kernel, as described in Section 2.3. The classifier is trained on the labeled dataset of positives and negatives and can then be applied repeatedly on unlabeled prediction datasets to classify genes as co-regulated by the same mechanism as the input dataset or not.