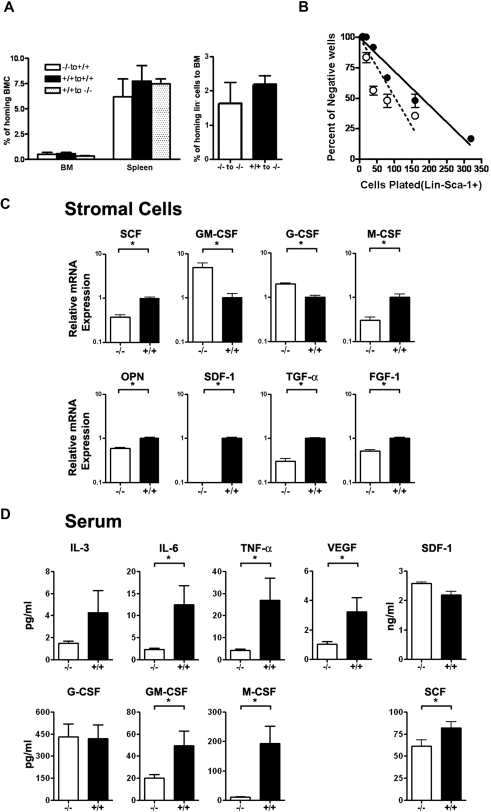
Figure 5.
Role of Id1 in the formation of the BM microenvironment. (A) The homing efficiency of Id1−/− and Id1+/+ BMC was assayed by the labeling of cells with CFSE. Staining was performed by incubating cells for 10 minutes in 37°C with 1 μmol/L concentration of CSFE. Then, 1.5 × 107 cells were injected into irradiated recipient mice. At 24 hours, recipient BM and spleen cells were harvested, and CSFE-positive cells were analyzed by flow cytometry (n = 2 for each genotype, P = .56). Lineage-negative (Lin−) hematopoietic cell homing was determined by transplanting 8.5 × 106 Lin− cells per mouse (n = 3 for each genotype, P = .46). (B) LTC-IC assays of mouse hematopoietic cells using primary BM stromal cells and limiting dilution analysis was used to compare the supportive function of Id1−/− (○—○) and Id1+/+ (●—●) BM-derived stromal cells. Wells containing clonogenic cell colonies were scored after 10 days of culture of Id1+/+ Lin−Sca-1+ BM progenitors with established stromal cells from Id1−/− or Id1+/+ and plotted as the number of wells that showed no growth for each cell dilution. The data are presented as representative data from 2 separate experiments. (C) Serum chemokine and cytokine concentrations (expressed as picograms per milliliter except SDF-1α, which is nanograms per milliliter) were measured and compared between 2 groups of age- and sex-matched mice (n = 21 for Id1−/−, n = 18 for Id1+/+, *P < .05). (D) Total RNA was isolated from cultured bone marrow–derived stromal cells and real-time PCR was used to measure mRNA. Relative mRNA units were normalized to glyceraldehydes-3-phosphate dehydrogenase levels. Data shown are the mean ± SEM in triplicate (*P < .05).