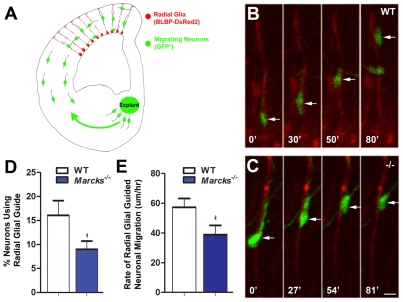
Fig. 5.
Marcks deletion disrupts radial glia-guided migration. WT and Marcks-/- E15.5 cortices were electroporated with BLBP promoter-dsRed2 plasmids to label radial glia (red). (A)GFP+ explants from the medial ganglionic eminence of Dlx5/6-CIE mice were then overlaid onto electroporated slices to enable neuronal migration on radial glial processes. Time-lapse imaging of these assays was used to monitor radial glia-neuron interactions. (B) Illustration of a migrating neuron (arrow, green) along a WT radial glial process (red). Time elapsed between observations is indicated in minutes. (C) Illustration of the altered migration of a neuron (arrow, green) on Marcks-/- radial processes (red). (D) Quantification of radial glia-neuron interactions in these assays indicates that fewer neurons initiate contact with and utilize MARCKS-deficient radial glial processes as migratory guides. (E) Compared with WT controls, the average rate of radial-glial-guided migration is significantly lower on Marcks-/- radial glia. Data shown are mean±s.e.m.; asterisk indicates significance when compared with controls at P≤0.01. Scale bar in C: 7.5 μm for B,C.