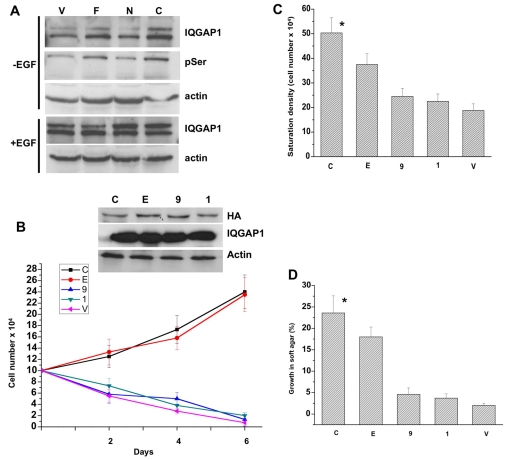
Fig. 4.
IQGAP1 phosphorylation and binding to CDC42 are required for transformation. (A) Immunoblots of equal amount of extracts from cells untreated (upper panels) or treated with EGF for 5 minutes (lower panels) immunoprecipitated and blotted with antibodies for IQGAP1 or phosphoserine (pSer). Actin was detected as a loading control. The blot represents three experiments with identical results. (B) Top panel, blot demonstrating equal expression levels of IQGAP1 mutants in total lysates of the NIH3T3 stable cell lines: C,IQGAP1-C; E, IQGAP1-C-S1443E; 9, IQGAP1-C-ΔMK24; 1, IQGAP1-C-S1443A. Actin and endogenous IQGAP1 were detected as loading controls. Lower panel, proliferation rate of mutant cells in low serum (1%) medium. Means ± s.e.m. for n=3 experiments are shown for three clones each done in duplicate (*P<0.001). (C) Lack of contact inhibition was measured as saturation density in high serum (10%) and expressed as mean ± s.e.m. for n=3 experiments for three clones each done in duplicate (*P<0.001). (D) Anchorage-independent growth for the mutants in soft agar was scored after 10 days as the percentage of colonies ≥50 μm in diameter. Error bars are means ± s.e.m. for n=3 experiments (*P<0.001). P values indicate significant difference between highest and lowest values.