Figure 4. Lipid remodeling and anandamide metabolism: analysis of phosphatidylethanolamine (PE) species.
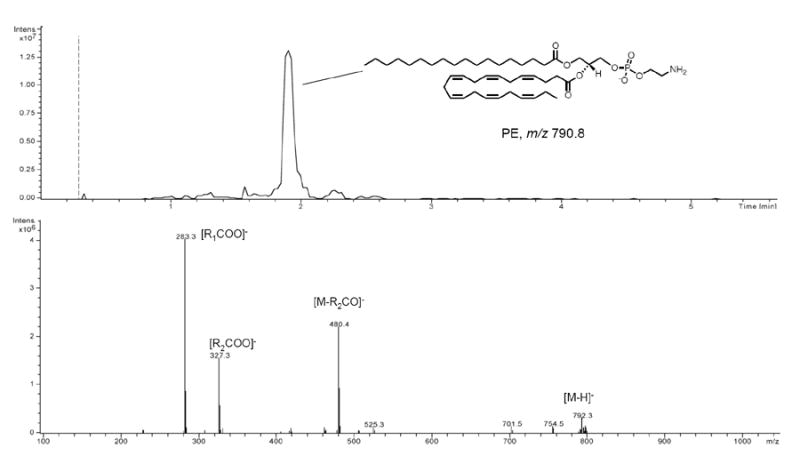
Representative LC/MS analysis of PE species in a human brain. LC/MS chromatogram (top) and MS2 fragmentation pattern using an ion trap mass spectrometer (bottom). PE species were detected as deprotonated molecular ions in the negative mode. In MS2, the most prominent fragments are the sn-2 lyso-PE in combination with the sn-1 and sn-2 carboxylate anions [90]. Sample characteristics are described in the text. Lipids were extracted from approximately 50 mg of brain tissue and resuspended in 0.1 ml of methanol. Injection volume was 10 μl. Separation was performed on a SB300 Poroshell column (Agilent-Technologies coating layer of 0.25 μm on total particle diameter of 5 μm) using a linear gradient of methanol in water containing 0.25% acetic acid and 5 mM ammonium acetate (from 85% to 100% of methanol in 5 min) at a flow rate of 1.0 ml/min with column temperature set at 50 °C. Capillary voltage was 4.5kV, skim1 -40V, and capillary exit -151V. N2 was used as drying gas at a flow rate of 12 liters/min, temperature of 350°C and nebulizer pressure of 80 PSI. Helium was used as collision gas. Abbreviations: R1=sn-1 aliphatic chain; R2=sn-2 aliphatic chain.
