Figure 9. Lipid remodeling for 2-AG: analysis of phosphatidylinositol (PI) and phosphatidylcholine (PC) species.
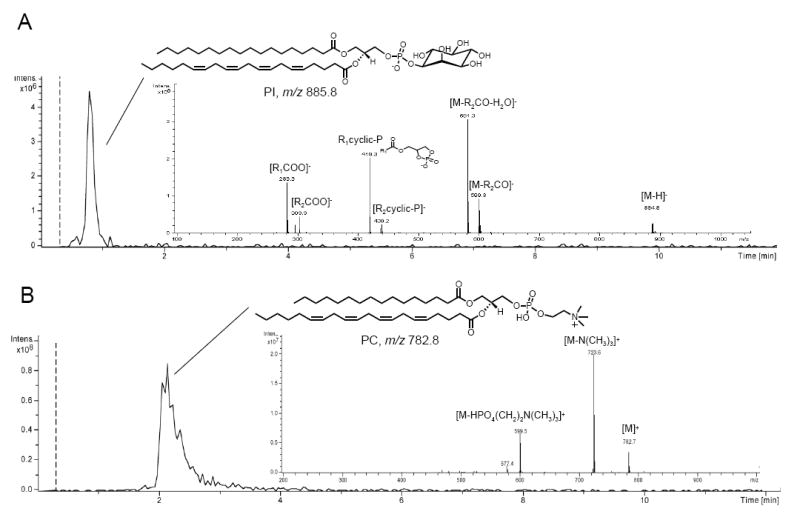
A, Representative LC/MSn analysis of 1-stearoyl,2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoinositol in a human brain. Sample characteristics are described in the text. LC/MS conditions in Fig. 4 legend. Lipids were extracted from approximately 50 mg of brain tissue and resuspended in 0.1 ml of methanol. Injection volume was 10 μl. In the negative ion mode PI was detected as deprotonated molecular ion. MS2 yielded the sn-2 lyso-PI together with the sn-1 and sn-2 carboxylate anions. Furthermore, the neutral loss of a ketene in combination with the neutral loss of the inositol head group yielded a putative cyclic sn-1 lysophosphatidic acid derivative. B, Representative LC/MSn analysis of 1-stearoyl,2-arachidonoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine in a human brain sample. Chromatographic conditions are described in Fig. 4 legend. PC was detected as protonated molecular ion in the positive ion mode. MS2 yielded product ions deriving from the neutral loss of the trimethylammonium and the phosphocholine head group. Abbreviations: R1=sn-1 aliphatic chain; R2=sn-2 aliphatic chain.
