Figure 3.
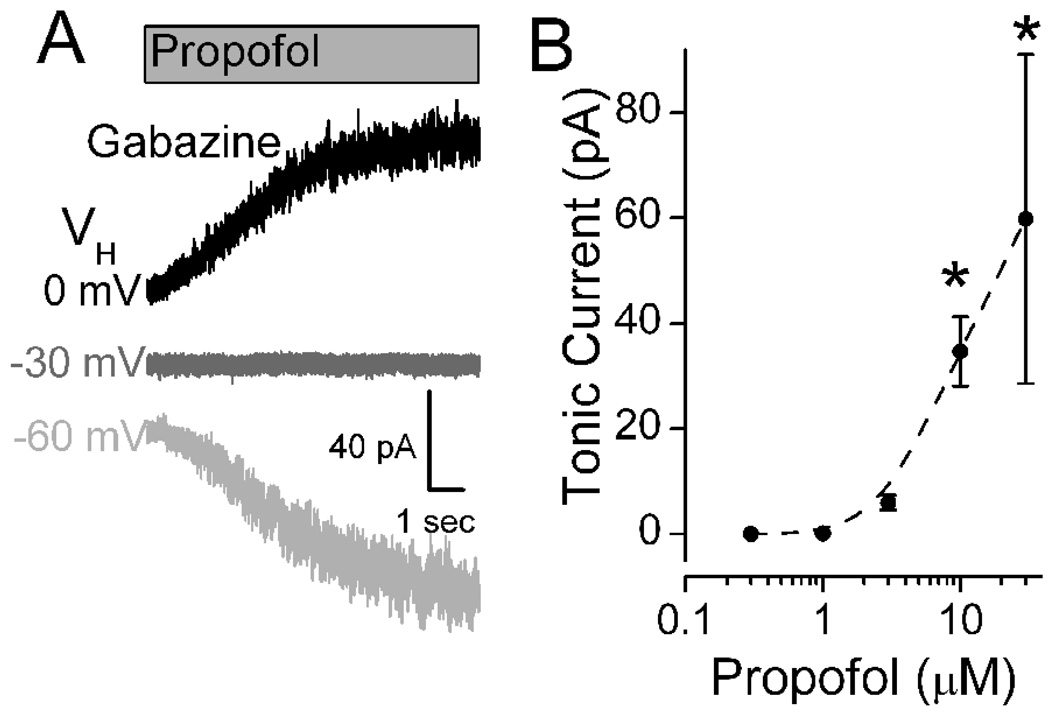
Propofol evoked a shift in the mean level of tonic current following block of phasic currents. A. Voltage dependence of propofol-evoked tonic current. All traces recorded from same cell in the presence of NBQX, AP5 and gabazine (6 µM), a combination that blocked all phasic synaptic events including sIPSCs. At VH = −60 mV, propofol (10 µM) evoked a slowly increasing tonic inward current, but that current was outward at VH = 0 mV. No current was observed at VH = −30 mV. Levels of VH are indicated by shading: black, gray and light gray as 0, −30 and −60 mV respectively. Under these experimental recording conditions, ECl was −30 mV. Traces measured in a single representative NTS neuron. Indicated potentials are corrected for the liquid junction potential.
B. Propofol increased the tonic inward current at VH = −60 mV in a concentration dependent manner. Data points represent the peak current means ± SEM for 4–19 different neurons. Asterisks mark significant differences in mean responses from Control (Repeated Measures ANOVA with Holm-Sidak method of post hoc pairwise comparisons at p<0.05).