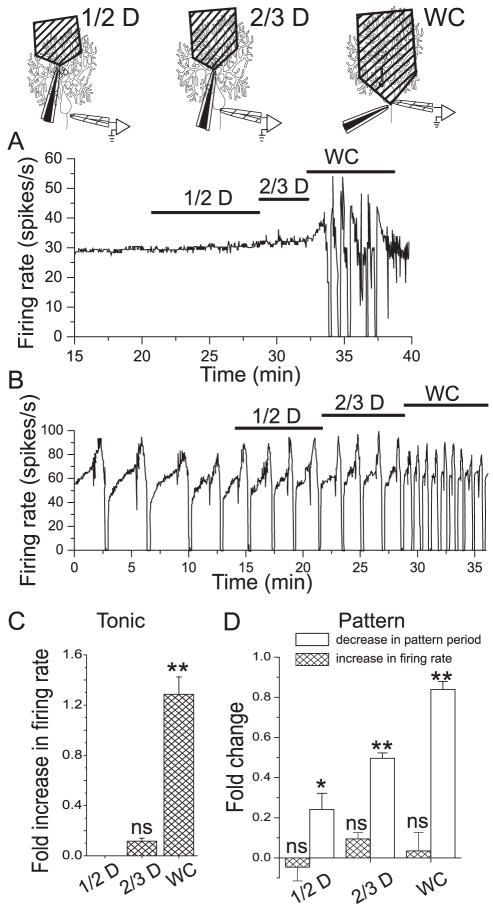
Figure 4. BK channels which control firing rate are localized to the soma of Purkinje neurons while BK channels which regulate the duration of the trimodal pattern are localized to both soma and dendrites.
Iberiotoxin (100 nM) was applied selectively via local perfusion to the distal half (1/2 D) or distal two thirds (2/3 D) of the dendrites or to the whole cell (WC). A, Average firing rate of a tonic firing neuron in response to local application of iberiotoxin. Application to the dendrites had no effect. B, Average firing rate of a neuron with the trimodal pattern of activity in response to local application of iberiotoxin. C, Average fold-increase in firing rate of tonic firing neurons following local block of BK channels. Block of CK channels to the distal ½ (no effect) or distal 2/3 of the dendrites (0.11 (± 0.02)-fold increase) did not significantly change the firing rate. Block of BK channels I the whole cell increased the firing rate by and average of 1.28 (± 0.14)-fold. Error bars are ± S.E.M., n=4. ns, value not significantly different from control. **, significantly different from 0 (p< = 0.001, by Oneway ANOVA). D, Average fold-increase in firing rate (hatched bars) and fold- decrease in pattern duration (open bars) in Purkinje neurons with the trimodal pattern of activity. Block of BK channels did not significantly increase firing rate. The mean fold-increases in firing rate were (1/2 D,) −0.05 (± 0.07), (2/3 D), 0.09 (± 0.03), and (WC), 0.04 (± 0.09). None of these values was significantly different from 0 (ns). Block of BK channels in the dendrites decreased the pattern period. Mean fold- decreases were 0.24 (± 0.08) (1/2 D), and 0.5 (± 0.03) (2/3 D). Application to the whole cell decreased the period 0.84 (± 0.04)-fold. Error bars are ± S.E.M., n=7. The changes were significant (*, p = 0.02, **, p = 0.001 by Oneway ANOVA).