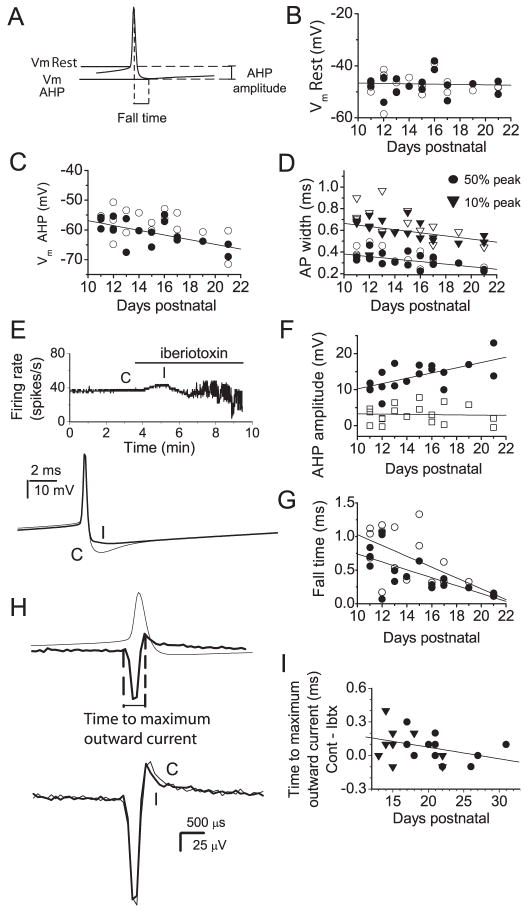
Figure 6. Contribution of BK channels to action potential waveform.
A–G, Whole cell current clamp recordings were obtained from spontaneously firing Purkinje neurons. Trains of 100–1500 action potentials were averaged and action potential waveforms analyzed from the average traces. A, The diagram shows parameters measured from the average action potentials. Vm Rest, membrane potential 500 μs prior to the peak of the action potential; Vm AHP, minimum membrane potential following action potential; AHP amplitude, Vm Rest - Vm AHP; fall time, time from peak of action potential to Vm AHP. The action potential width at 10 %and 50 % of the difference between the peak and Vm Rest was also measured. B, Vm Rest vs. age for individual Purkinje neurons under control conditions (filled symbols) and in iberiotoxin (open symbols). Linear regression fit to the control data shows no correlation of Vm Rest with age of the animal (R2=0.053, p=0.83). C, Vm AHP vs. age for all neurons tested. A linear regression fit to the control values shows a clear correlation between the AHP and age (R2=0.69, p=0.008). D, Action potential width at 10% and 50 % of peak value vs. age. Closed symbols show values under control conditions and open symbols values for the same neurons in iberiotoxin. Linear regression fits to control data show a clear correlation between age and action potential width (R2=0.65, p=0.04 at 10%; R2=0.68, p=0.008 at 50%). E, Effect of BK channel block on a spontaneously active Purkinje neuron. Top panel: Average firing rate vs. time. Application of iberiotoxin caused an initial increase in firing rate followed by irregular firing. Bottom panel: Average action potentials under control conditions (C) and in the presence of 100 nM iberiotoxin (I) taken at the times indicated in the top trace. BK channels contributed to an AHP which persisted for several ms following each action potential. F, AHP amplitude vs. age. Values for individual cells are shown for the total AHP (circles) and for the iberiotoxin-sensitive component of the AHP (squares). Linear regression fits show a clear correlation between total AHP amplitude and age (R2=0.67, p=0.006) but no correlation between the iberiotoxin-sensitive component of the AHP and age (R2=0.043, p=0.87). G, Fall time vs. age. Values for individual cells under control conditions (filled symbols) and in iberiotoxin (open symbols) are shown. Linear regression fits show a correlation between fall time and age for both sets of data. (R2=0.69, p=0.005 for control; R2= 0.63, p= 0.005 in iberiotoxin). The slope increases from −0.06 ms/day in control conditions to −0.08 ms/day in iberiotoxin indicating that BK channels make a larger contribution to fall time at younger ages. H, I, Extracellularly recorded spike waveforms were analyzed. Averages of 100–1500 action potentials were generated. H, Upper panel: Action potential recorded in whole cell mode (thin trace) and an extracellular spike waveform (thick trace) which shows the temporal correlation between potential changes recorded with an extracellular electrode and the action potential waveform. The positive peak of the extracellular recording corresponds to the time at which the rate of membrane repolarization, hence the net outward current, is maximal. Lower panel: Extracellular spike waveforms recorded under control conditions (thin trace) and in iberiotoxin (thick trace) shows that block of BK channels causes a decrease in the time to maximum outward current. I, The difference between the time to maximal outward current in control conditions and the time to maximal outward current in iberiotoxin vs. age. Values for individual cells which fired tonically (triangles) and those with the trimodal pattern of activity (circles) are shown. A linear regression fit shows a negative correlation between the contribution of BK channels to the maximum outward current and age (R2=0.36. p=0.11).