Fig. 5.
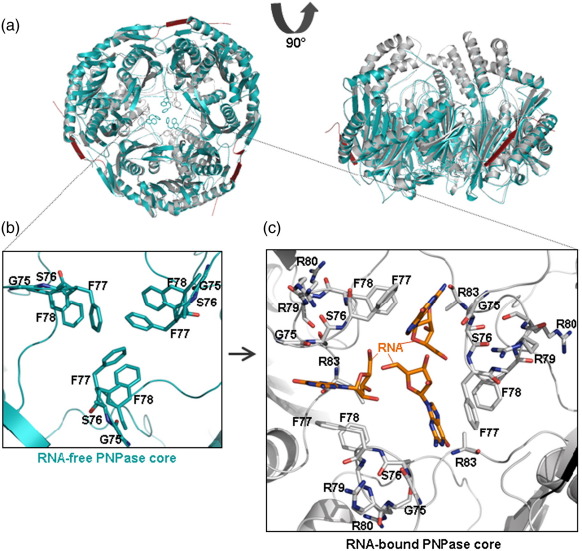
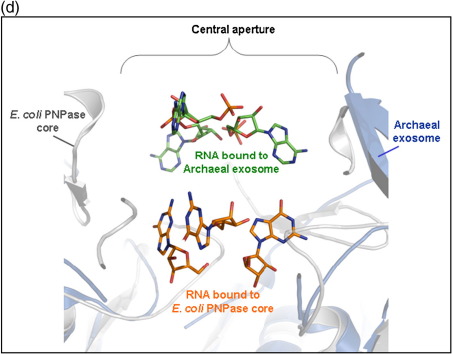
Structural changes associated with RNA binding to the PNPase core. (a) An overlay of the RNA-free (cyan) and RNA-bound (grey) forms of PNPase core viewed down the molecular 3-fold axis (left) and perpendicular to it (right). In the view on the right, the helical domain is on the top of the torus, and the S1 and KH domains (not shown) are on the bottom. (b) Expanded view of the central channel aperture in the RNA-free form. The aperture is occluded by the F77 and F78 side chain of the FFRR loop in this apo-structure, but the loop is less well ordered in the Mn2+apo structure and in the apo-structure reported by Shi et al.29 (c) The same view as in the left-hand panel but in the RNA-bound form; this shows that the aperture has dilated. It is not clear whether all three RNA-binding sites could be accommodated simultaneously. (d) RNA binds to the central aperture of both E. coli PNPase core (orange) and the S. solfataricus archaeal exosome (green), albeit at a different depth in the central channel. The view is with the molecular 3-fold oriented vertically.