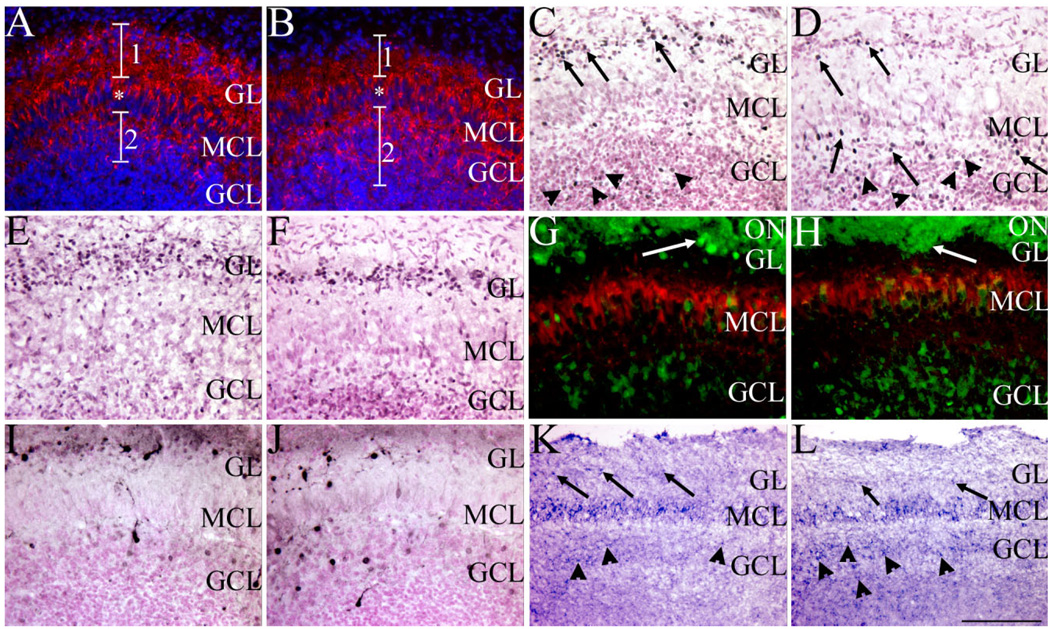
Fig. 7.
Sall3 is required for the terminal maturation of olfactory interneurons. GAD65/67 (red; A,B), Pax6 (black; C,D), ER81 (black; E,F), calretinin (green)/reelin (red; G,H), calbindin (black; I,J), and Nurr1 (blue; K,L) expression in the olfactory bulb in coronal (A–J) and sagittal (K,L) sections at P0.5 of control (A,C,E,G,I,K) and Sall3 mutant (B,D,F,H,J,L) animals. Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue; A,B) and nuclear fast red (C–F,I,J). Fewer GAD65/67-expressing cells were observed in the GL in Sall3 mutant animals, accompanied by more positive cells in the GCL (B). 1 and 2 demarcate the GL and GCL, respectively; asterisk indicates the GAD65/67-positive projections through the MCL (A,B). In control animals, large Pax6high-expressing cells were observed predominantly in the GL (arrows, C), and small Pax6low-expressing cells were located in the GCL (arrowheads, C). In Sall3 mutant animals, fewer large Pax6high-expressing cells were observed in the GL (arrows, GL, D), and more large Pax6high-expressing cells were observed in the GCL (arrows, GCL, D). No gross difference was observed in the numbers of small Pax6low-expressing cells (arrowheads, D). A decrease in ER81-expressing cells was observed in the GL in Sall3 mutant animals (F). Similar alterations were observed with calretinin and calbindin populations in Sall3-deficient animals (H,J). Glomeruli-like structures were observed in control (arrow, G) and Sall3 mutant animals (arrow, H). Nurr1 expression was observed in the GL (arrows), MCL, and GCL (arrowheads) of control (K) and Sall3 mutant (L) animals, although an increase Nurr1 expression was observed in the GCL in the absence of Sall3 (L). GCL, granule cell layer; MCL, mitral cell layer; GL, glomerular layer; ON, olfactory nerve. Scale bar = 100 µm for A–F,I,J; 75 µm for G,H; 200 µm for K,L.