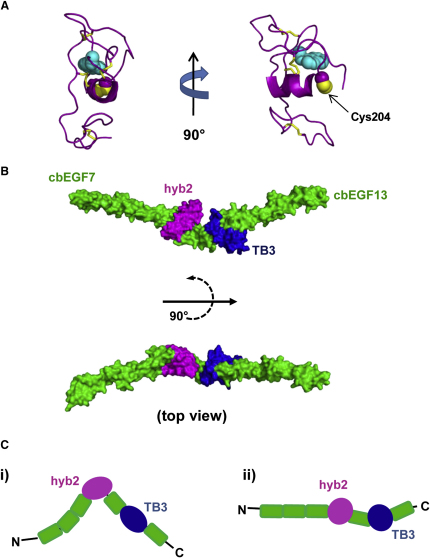
Figure 6.
Models of Other Fibrillin-1 Regions
(A) A model of domain hyb1, using the coordinates of hyb2 from the cbEGF9-hyb2-cbEGF10 structure, shows that Cys204 is likely to occur at an exposed position at the N terminus of the domain's central α helix.
(B) Molecular modeling data suggest that the region from cbEGF7 to cbEGF13 is generally linear, with domains hyb2 and TB3 inverted with respect to each other. Models were created using Modeler software (Eswar et al., 2007) and the coordinates of the structures determined for fibrillin-1 fragments cbEGF12-cbEGF13 (Smallridge et al., 2003), cbEGF32-33 (Downing et al., 1996), and cbEGF22-TB4-cbEGF23 (Lee et al., 2004).
(C) An earlier interpretation of the structure of the cbEGF7-cbEGF13 region (i), based on SAXS data (Baldock et al., 2006), suggested a V-shaped bend in the region of the hyb domain. High-resolution studies of hyb and TB interactions with adjacent domains (ii) suggest a more linear organization, highlighting the influence of high-resolution constraints on models to explain microfibril length and extensibility.