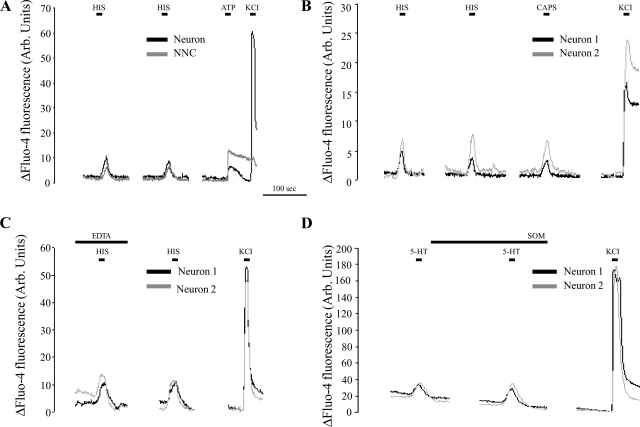
Fig. 4.
Representative recordings of the normalized changes in fluo-4 fluorescence measured in spinal neurons and nonneuronal cells (NNC) in vitro. A: both neurons and NNC displayed a calcium-dependent activation in response to short-term HIS stimulation. After a 2-min interval, repeated HIS stimulation evoked similar responses without a clear reduction in response amplitude. At the end of the experiment, viable neurons were identified by stimulation with a high K+-containing solution, NNC by stimulation with 50 μM ATP. B: virtually all neurons responsive to HIS and 5-HT also responded to capsaicin (CAPS) stimulation. C: determining the source of the calcium influx in neurons upon HIS- or 5-HT stimulation. For the time indicated, the physiological solution was replaced by a buffer without CaCl2 and containing 1 mM EDTA. Stimulation with 10 μM HIS during this period evoked responses that were not different from the ones after a 2-min interval during which the cells were again superfused with normal physiological solution. D: determining the short-term effects of SOM on neuronal activation by 5-HT. Following the first stimulation, cells were perfused for 2 min with physiological solution containing 10 μM SOM, after which the cells were once again stimulated with physiological perfusate containing both 5-HT and SOM. No decrease in the number of 5-HT-activated neurons or in the evoked response amplitudes was observed. Arb., arbitrary.