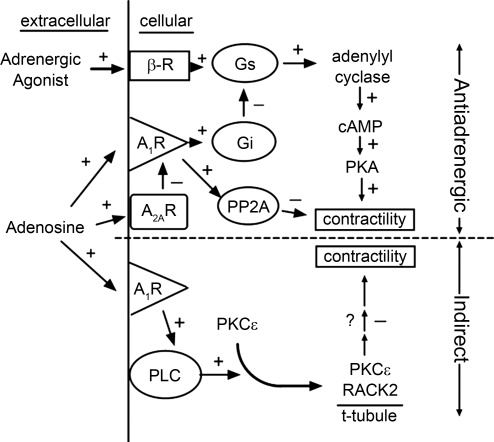
Fig. 6.
Schematic depicting proposed mechanisms by which the nucleoside adenosine elicits an adenoprotective action in the myocardium. Adenosine affords adenoprotection against overstimulation by adrenergic agents via two mechanisms: 1) the direct attenuation of the adrenergic signaling pathway (anti-adrenergic action; top); and 2) the reduction of contractile responsiveness independently of this pathway (indirect; bottom). β-R, β1-adrenergic receptor; Gs and Gi, stimulatory and inhibitory G proteins, respectively; PP2A, protein phosphatase 2A; PLC, phospholipase C; + and − depict an activation and inhibition, respectively, in the subsequent event.