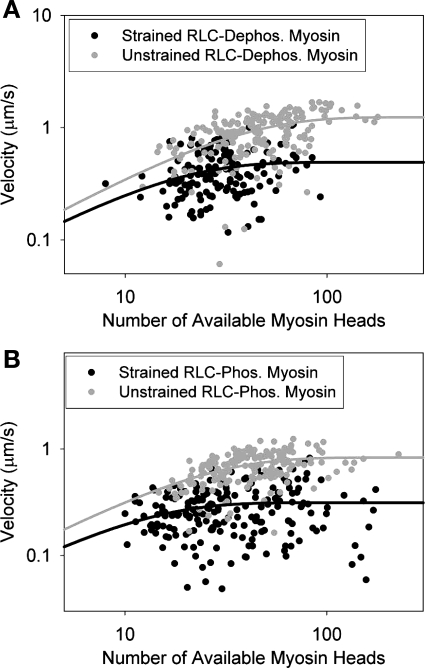
Fig. 3.
Comparison of the effect of applied strain on the duty cycle on RLC-dephosphorylated (A) and RLC-phosphorylated myosins (B). Each point represents the average sliding velocity of a single actin filament across 5–10 video frames; 145 actin filaments were followed for RLC-dephosphorylated myosin, and 204 actin filaments were followed for RLC-phosphorylated myosin. The duty cycle for strained dephosphorylated myosin was 6.8 ± 1.6%, and the duty cycle for strained phosphorylated myosin was 9.2 ± 2.0%. These measured duty cycles are ∼2-fold higher than the measured unstrained duty cycles.