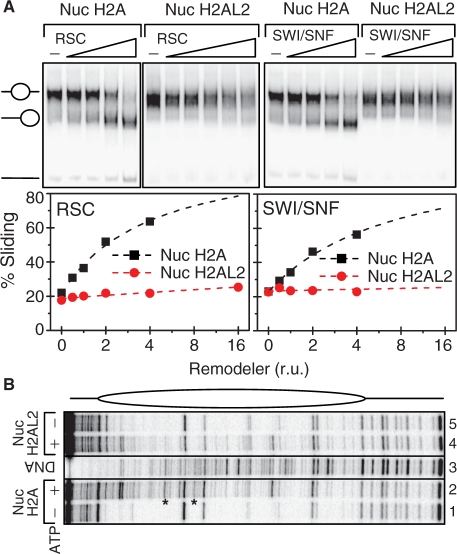
Figure 8.
The presence of H2AL2 interferes with both SWI/SNF and RSC nucleosome remodeling and mobilization. (A) Nucleosome mobilization assay. Centrally positioned conventional and H2AL2 nucleosomes were reconstituted on a 32P-end-labeled 255 bp 601 DNA fragment and used for either RSC (left panel) or SWI/SNF (right panel) mobilization assay. Both types of reconstituted nucleosomes were incubated for 40 min at 30°C with increasing amounts of the respective remodeler in the presence of ATP. After arresting the reaction, the samples were run on a 5% native PAGE (the conventional and H2AL2 RSC-treated nucleosomes were run on two different gels and the data are presented in two separate panels). The center and the end-positioned (slid) nucleosomes and free DNA are indicated. The lower part of the figure shows the quantification of the data. (B) DNase I footprinting of RSC remodeled conventional and H2AL2 nucleosomes. Both centrally positioned conventional and H2AL2 particles, reconstituted on a 32P-end-labeled 255 bp 601 DNA fragment, were treated with the highest amount of RSC used in the mobilization reaction as described in (A). After arresting the remodeling reaction the samples were digested with DNase I, the cleaved DNA was purified and run on an 8% sequencing PAGE. A schematic of the nucleosome is shown in the upper part of the figure. Lane 3, showing the digestion of the naked DNA, was not adjacent to lanes 2 and 4 in the original gel, and was thus demarked accordingly.