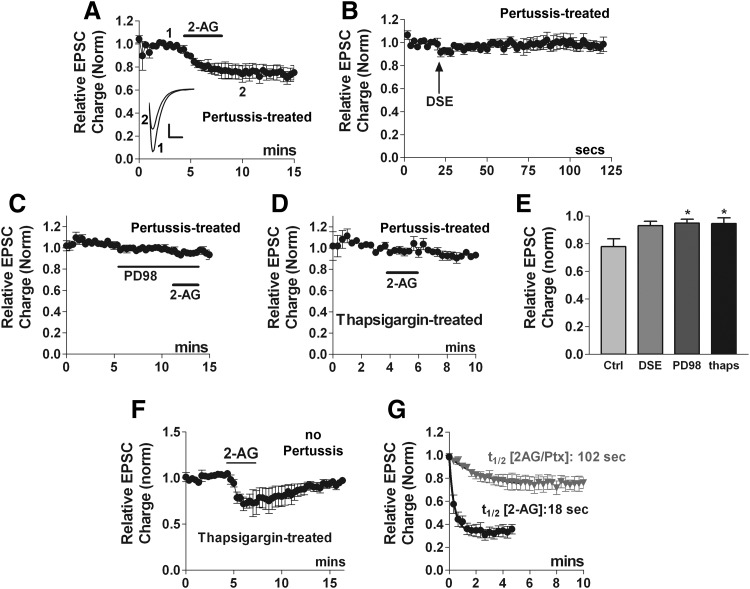
FIG. 7.
2-AG induces autLTD in a pertussis toxin-independent manner. A: 2-AG (5 μM) inhibits EPSCs even after pertussis toxin treatment (overnight, 400 ng/ml). Inset: sample EPSC traces at time points indicated, before (1) and after 2-AG-induced LTD (2). Scale bars: 1 nA, 10 ms. B: in the same cells as A, DSE is abolished by pertussis toxin treatment. C: MEK inhibitor PD98059 (PD98, 20 μM) blocks pertussis-toxin independent 2-AG inhibition. D: Ca-ATPase inhibitor thapsigargin (1 μM, >20mins), also blocks pertussis-toxin independent 2-AG inhibition. E: bar graph summarizes results from A, B, and D. F: averaged time course indicating that in cells treated with thapsigargin alone, 2-AG inhibition reverses fully. G: t1/2 values are calculated from the time courses from Figs. 7A (2AG/pertussis) and 6E (2AG) emphasizing the difference in kinetics between EPSC inhibition by 2-AG signaling via pertussis-toxin (PTX)-independent and -dependent pathways. *, P < 0.05 by 1-way ANOVA with Dunnett's post hoc test vs. control inhibition (2-AG after PTX treatment).